A Study to Assess the Level of Knowledge Regarding Assessment and Management of Myocardial Infarction among Nursing Staff in Selected Hospital at Mysore
Mrs. Lakshmi KN*
Principal, Vikram College of Nursing, Mysore, India
Submission: July 25, 2018; Published: August 05, 2018
*Corresponding author: Mrs. Lakshmi KN, Principal, Vikram College of Nursing, Mysore, India, Email: saraswathimysores803@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Mrs. Lakshmi KN. A Study to Assess the Level of Knowledge Regarding Assessment and Management of Myocardial Infarction among Nursing Staff in Selected Hospital at Mysore. JOJ Nurse Health Care. 2018; 8(5): 555750. DOI: 10.19080/JOJNHC.2018.08.555750.
Abstract
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is the major cause of morbidity and mortality burden in the world. Young patients with CAD are specific subset of population requiring attention. A variety of possible contributing factors that include substance abuse, coronary artery anomalies, oral contraceptive use in young women have been implicated for the pathogenesis of myocardial infarction [1].
Statement of the problem: A study to assess the level of knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff in selected hospital at Mysore.
Objectives of the study: 1 To assess the level of knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff [2]. To find the association between knowledge scores regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff with their selected personal variables.
Methodology:Descriptive design was used for the study. Sample of 60 nursing staff was selected by convenience sampling technique. Data was collected by administering personal proforma and structured knowledge questionnaire regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction.
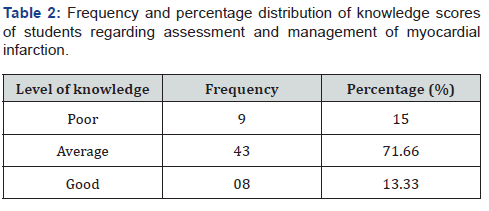
Results: 9(15%) had poor knowledge, 43(71.66%) had average knowledge and 8 (13.33%) had good knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff. 1.5.
Conclusion: Nurses need to updated in their knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction by conducting continuing nursing educational programs
Keywords:Nursing staff & Assessment; Management of myocardial infarction
Introduction
The world health organization has defined Ischemic heart disease as myocardial function impairment due to imbalance between coronary blood flow and myocardial requirement the most common cause being atherosclerosis. Nurses play a strong role in helping patients reduce their risk for disease and make informed lifestyle changes. Reliability of the nurses is critical for them to serve as role models and educators [3]
Need for the study
relation to heart disease found that Indians have the highest risk of coronary heart disease, with rates three to four times higher than Americans, six times more than the Chinese and 20 times more than the Japanese. In North India, 7-10% of people have coronary heart disease while the prevalance is as high as 14% in South India. The prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) has progressively increased in India during the later half of the half century and is the major cause of morbidity and mortality burden in the world. Global burden of disease study estimate that by the year 2020, the burden of atheroembolic cardiovascular disease in India would surpass that in any other region in the world [4].
Statement of the Problem
A study to assess the level of knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff in selected hospital at Mysore.
Objectives of the Study
i. To assess the level of knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff
ii. To find the association between knowledge scores regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff with their selected personal variables.
Hypothesis
H1: there will be a significant association between knowledge scores regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff with their selected personal variables.
Assumptions
Nursing staff may have some knowledge and skill regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction.
Methodology
a) Research approach and Design: Descriptive research design
b) Variables of the study: knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction.
c) Setting: Vikram Hospital, Mysore
d) Population: nursing staff
e) Sample and sample size: 60 nursing staff
f) Sampling technique: Nonprobability Convenience Sampling technique
g) Criteria for sampling:
h) Inclusion criteria:
Nursing staffs who are
a) Available at the data of data collection
b) Willing to participate
Exclusion Criteria
Nursing staff who are working in administrative sections
Instrument Used for Data Collection
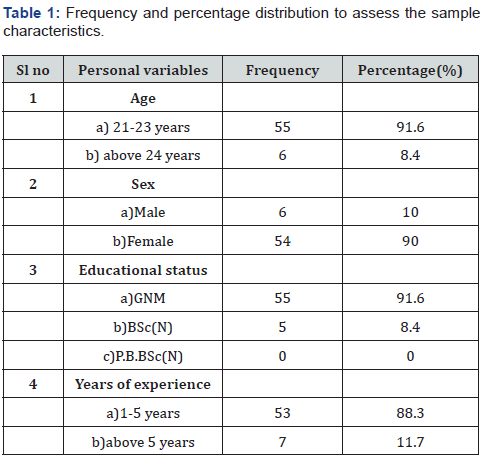
I. Section 1: Personal proforma to assess the personal variables such as age, sex, educational status and years of experience.
II. Section 2: structured knowledge questionnaire to assess the level of knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction which includes meaning, causes, risk factors, symptoms, warning signs and assessment, medical and surgical management of MI
Scoring
Poor knowledge -0-10
Average knowledge 11-20
Good knowledge 21-30
Data Collection Procedure
Formal administrative permission was obtained from Hospital prior to data collection. Informed consent was obtained from the samples. 60 samples were selected by using non probability convenience sampling technique. Data was collected by administering personal proforma and structured knowledge questionnaire regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction. Staffs took 30 min to fill the questions. Data collection process was terminated by thanking the samples.
Results
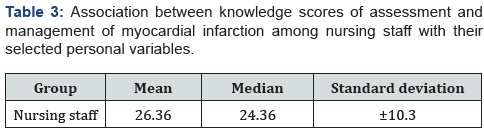
I. Section 3: Association between knowledge scores of assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff with their selected personal variables.
There was no significant association between knowledge scores of assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff with their selected personal variables (Tables 1-3).
Conclusion
The present study revealed that knowledge scores of assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff. 9(15%) had poor knowledge, 43(71.66%) had average knowledge and 8 (13.33%) had good knowledge among nursing staff.
Recommendations
i. Similar study can be conducted by using true experimental approach.
ii. A study can be conducted to assess the effectiveness of STP on knowledge regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among nursing staff.
iii. Study can be done to compare the knowledge of staff regarding assessment and management of myocardial infarction among private and government hospitals.
References
- Bahl VK, Prabhakaran D, Karthikeyan G (2001) Coronary Artery disease in Indians. Indian Heart J 53(6): 707-713
- Rissan HS, Kishore S, Trehan N (2001) Coronary Artery disease in young Indians: The Missing Link. JIACM 2(3).
- Eugene Braun Wald, Joseph Loscalzo (2008) Ischaemic Heart Diseases. Harrison’s Principle of Internal Medicine (18th edn), Mc Graw Hill, Henry N Ginsberg, Ira J Goldberg, E. Braun Wald (Eds.): Disorder of Lipoprotein metabolism in Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine.
- NeelimaChoure, Harish K Chandrawanshi, Mithun S Rajput, Suneyna Sehgal, Maya E Patliya, et al. (2015) The effectiveness of self instructional module on cardiac rehabilitation. International Journal of Nursing Sciences 2(3): 317-323.






























