Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on Jammu and Kashmir Economy
Arshad Bhat*
Rajiv Gandhi Chair in Contemporary Studies on Livelihood and Food Security, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir
Submission: September 23, 2023;Published: October 30, 2023
*Corresponding author: Arshad Bhat, Rajiv Gandhi Chair in Contemporary Studies on Livelihood and Food Security, Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology of Kashmir, India Email: bhatarshad09@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Arshad B. Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on Jammu and Kashmir Economy. JOJ Hortic Arboric. 2023; 4(1): 555629. DOI: 10.19080/JOJHA.2023.04.555629.
Abstract
The Coronavirus pandemic of 2020-21 was hazardous and disastrous occasion throughout the entire existence of India. The situation of the 2020-21 Coronavirus in Jammu and Kashmir eclipsed the disaster of 1908 and the bubonic plague calamity of the principal decade of the 20th century. More than 1,976 people died between March 2020 and 2021. This paper presents the impact of covid -19 on the overall food production, the availability of cold storage units and the need-based inputs availability in the UT. The paper also presents a quantitative analysis of consumption of different food items during and after lockdown in the UT. The paper assesses the timely rise in the covid cases and the rising number of deaths state wise accordingly. The results revealed that there was a rise in fruit production from 2.14 -2.54 ‘000 MT during the pandemic period in the UT. The paper also highlights that there is an increase in horticulture production in India from 166.94 - 326.48 million tons.
Keywords: Social stratification; Miseries; Woes; Aftermath; Recovery; Expenses.
Introduction
Coronavirus pandemic caused 2.72 million of fatalities all through the globe. The pandemic tainted 124 large number of individuals around the world [1]. Maharashtra remained perhaps the most perceptibly horrendous hit states with a normal mortality of 52996 people [2]. Jammu and Kashmir got most regions with a contamination of 1.02 percent per people. In any case these dazzling estimations, the social and monetary results of this disease rate alongside a little bed and ventilator limit in the UT of Jammu and Kashmir remained commonly faultless. Thus, this transforms into the point of convergence of this examination.
In an associated vein, a couple of examiners delved into the consequences of 2020-21 Coronavirus pandemic across different countries [3]. highlighted the dangerous effects of pandemic on babies whose mothers experienced flu during pregnancies in the United States. In the Indian, a few specialists have uncovered the monetary results of the 2020-21 Coronavirus pandemic on neighborhood peoples [4]. Many existing assessments have focused in on the epidemiological settings and section impacts of the Coronavirus scourge. [5] attempt to unravel the inspiration driving why a couple of zones were more disposed to Coronavirus than others. It was found that regions with higher people thickness are more disposed to a higher demise rate from flu because of the connected straightforwardness of dispersal [6]. [7] drove a lab test guinea pig, which uncovers that low relative or complete moisture favors the spread of pandemic.
Methodology
The examination depended on truth finding and the data was acquired from various credible sources. Verifiable perspective on the prior pandemics were thought to lay a sound base for the current examination. The information was gotten from various reports and divisions and proper devices and strategies were utilized to compute the outcomes and derivations were drawn on consistent premise. Forecasts were made dependent on the rationale followed by various logical examinations. The distinctions were worked out by dealing with suggested levels of admission and accessibility in the UT. The development was determined by utilizing the accompanying formulae.
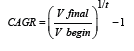
Were,
CAGR= compound annual growth rate
Vbegin = beginning value
Vfinal = final value
t= time in years
Jammu and Kashmir UT and Covid-19 Pandemic
Humanity has routinely experienced attacks, Coronavirus like ailments virtually all through its recorded history [8]. Covid pandemics have cleared across tremendous regions of the world, routinely leaving enormous peoples decimated. Hippocrates distinguished an infection with comparative clinical highlights to covid-19, around 400 years before the introduction of the threat to loss of life from the infection stayed the most exceedingly terrible in the chronicles of the UT. The danger to death toll from the disease remained the most incredibly horrible in the annals of the UT. The passing speed of Coronavirus outflanked other scourge sicknesses considering its modestly short time frame of infectivity and the resulting end rate. The Coronavirus epidemic fumed for around over a year, leaving around 128,000 people contaminated in the UT [9].
The passing speed of Coronavirus ailment when in doubt depends upon the mutagenic properties of the contamination. The passing rate was expressly higher between the ages of 40 or more, while pregnant women experienced more the plague of Coronavirus of 2020-21 in the UT. A few experts have uncovered that the inclination for young adults is inferable from the enrolment of cytokine storm by the Coronavirus contamination. For instance, [10] saw that preposterous induction of the immune structure resulted in more deaths in old individuals. Thus, young adults with a more grounded safe system were more disposed to pass on from the disorder in the 2020-21 pandemic. The Coronavirus contamination goes through dreary changes, after which it ends up being more unsafe and spreads rapidly, with calamitous mortalities. The infection was communicated from the travelers of Saudi Arabia and Iran, later this infection spread through visiting of family members to these pioneers and further association with the relatives.
Covid-19 in Jammu and Kashmir UT and its Overall Picture
The Covid contamination (Covid-19) has influenced each piece of life like business establishment, guidance, economy, religion, transport, work, entertainment, food security, sports, etc. The scene is a critical destabilizing risk to the overall economy. Monetary expert knowledge unit has gauge that markets will remain temperamental until a clearer picture emerges on the conceivable outcomes. One check from an expert at Washington University in St. Lois gave $3000+ billion impacts on the world's stock organization that could keep going up to two years [11]. Jammu and Kashmir did not endure colossally among different locales. From third March 2020 to eighteenth March 2021, 0.02 percent of its populace had died from the Coronavirus pandemic. The green items particularly apple which was lying in CA stores from November 2019 doesn't reach to the reasonable business sectors and because of danger of cold and hack customers limited to burn-through new organic products during the pinnacle of the Coronavirus all through the nation also in the U.T. coming about a tremendous misfortune to the producers. As indicated by Directorate of Information and Public Relations (DIPR), the scourge of the 2020-21 Coronavirus flare-ups outperformed past episodes of plague and jungle fever. Table 1 shows that the pace of covid-19 Infection was 1.02 percent which was higher than the public normal (0.95 %) and yet the recuperation rate (1.00 %) was superior to the public normal (0.90%).

Source: JHU CSSE COVID-19 Data, March 17, 2021
Covid-19 pandemic in Jammu and Kashmir UT and Central handling
These impacts are not bound to trade and business works out; the provincial region endured genuinely contemplating the agrarian commonness of Jammu and Kashmir, unequivocally during the hour of the eruption. Enormous disease of Coronavirus came about into extreme absence of workforce as the moved workforce returned to their local spots. Because of this work lack happened as well as the wages of neighborhood work likewise expanded. These factors set off the deficiency of some cultivating produce and loss of creation and usefulness. Because of this these elements, the agribusiness and unified areas in the locale confronted a difficult time as far as accessibility of data sources and work, which came about into loss of creation and bad quality produce during the season which was validated by the apple produce of the year 2020 having high irritation invasion and sickness ridden. Table 2 records the creation of significant food-grains and rural results of the UT opposite India.
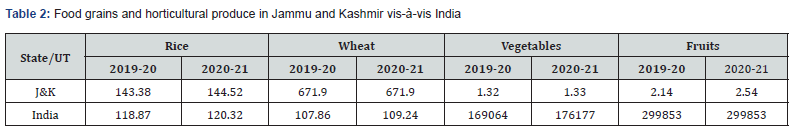
Rice and wheat production in MT, Vegetables and fruits, production in ‘000 MT
Source: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Govt. of India.
As exhibited in table 2, it appears to be that there is no critical impact on the creation of major farming and agricultural produce in India and Jammu and Kashmir. In any case, it is especially pertinent to note here that even though creation has not endured which a positive sign and yet the nature of the produce was not sufficient of fulfilment and furthermore the produce couldn't reach to the reasonable mandis and market with the outcome the maker in the year needs to expose an enormous misfortune. Toward the day's end, exhaustion of survivors upset key developing cycles like planting and gathering of yields similarly as the planning of property produce.
Table 3 shows the general situation of agrarian and plant execution in India. From the table due to Coronavirus pandemic there is not really any effect on the by and large food grains and green creation of the country. The foodgrains and green creation shows increment with an accumulate yearly development pace of 0.030 and 0.049 percent individually from 2004-05 to 2020-21.
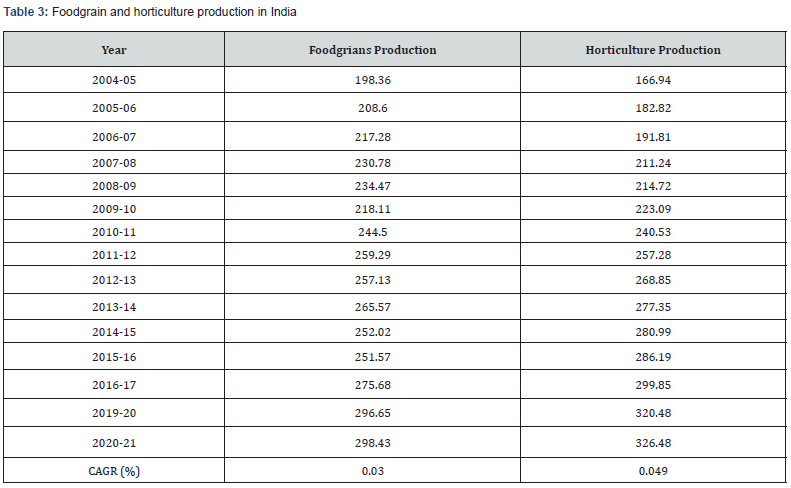
Source: Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare
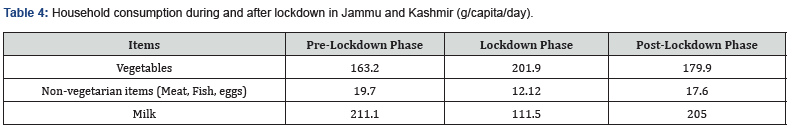
During the lockdown stage in UT, the utilization of food things like vegetables and other non-veggie lover things shows an alternate pattern. From the table it very well may be anticipated that the utilization of vegetables has expanded in the lockdown period in view of the non-accessibility of the non-veggie lover things attributable to the conclusion to street transport and markets in the UT. The utilization of the relative multitude of recorded things in table 4 came to the ordinary or considerably higher than that once the lock down was finished in a steady and stepwise savvy way.
Conclusion
Jammu and Kashmir experienced impressive warmth and agony of pandemic of 2020-21. The public authority (focal and UT) was surprised for the 2020-21 Coronavirus pandemic in Jammu and Kashmir. The causes remained dim and canvassed stealthily. This paper concludes that there was no significant impact of covid -19 on the overall food production in the UT, the smaller number of CA stores though created a situation of insecurity in the UT, but due to early stage of fruit bearing it couldn’t add too much to the woes of the growers. The paper also concluded that compared to other states the causalities in the Ut were not so high which could have created havoc in the Ut despite having dearth in health infrastructure. The results concluded that covid-19 has not affected the fruit production in the country so is the case with UT as well which is marked by the overall increase in horticultural production in the country [12,13].
References
- Worldometer (2021) Covid-19 Coronavirus Pandemic.
- Sanjay B (2020) The Social Impact of the COVID19 Pandemic. Issue Briefs and Special Reports.
- Valeria S, Davide A, Vincenzo A (2020) The Psychological and Social Impact of Covid-19: New Perspectives of Well-Being, Frontier in Psychology 11.
- Maria N, Zaid A, Catrin S, Ahmed K, Maliha A, et al. (2020) The socio-economic implications of the coronavirus pandemic (Covid-19): A review, International Journal of Surgery 78: 185-193.
- Abhishek S (2020) Covid-19 and its impact on Indian society.
- Hill K (2009) Influenza in India 1918: the epicentre of an epidemic.
- Shaman J, Kohn M (2009) Absolute humidity modulates Covid-19 survival, transmission, and seasonality. 106(9): 3243-3248.
- Hirsch A (1883) Handbook of Geographical and Historical Pathology. The New Sydenham Society, London.
- Chandra S, Kuljanin G, Wray J (2012) Mortality from the influenza pandemic of 1918-1919: The Case of India. Demography 49(3): 857-865.
- Lin MJ, Liu EM (2014) Does in utero exposure to Illness matter? The 1918 Covid-19 epidemic in Taiwan as a natural experiment. Journal of Health Economics 37(8181): 152-163.
- Vainavi A (2020) Impact of Covid-19 on Society and Environment.
- UNDP (2020) COVID-19: Socio-economic impact.
- WHO (2020) Impact of Covid-19 on people’s livelihoods, their health, and our food systems.






























