Uncovering the Impact of Age and Season on Various Types of Skin and Associated Skin Issues: A Survey Analysis
Uday Bhosale1, Prajakta Sapre1, Chaitanya Nallan2 and Shoaeb Mohammad Syed3,4*
1Scientist and Formulator, R&D, IncNut Lifestyle Pvt. Ltd., India
2Co-founder and CEO, IncNut Lifestyle Pvt. Ltd., India
3Consultant, Scientific Writing, IncNut Lifestyle Pvt. Ltd., India
4Associate professor, Dayanand College of Pharmacy Latur, India
Submission: February 05, 2024;Published: February 19, 2024
*Corresponding author: Shoaeb Mohammad Syed, Associate professor Dayanand College of Pharmacy Consultant, Scientific Writing, IncNut Lifestyle Pvt. Ltd, India, Email: ybccpsh@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Uday B, Prajakta S, Chaitanya N, Shoaeb Mohammad S. Uncovering the Impact of Age and Season on Various Types of Skin and Associated Skin Issues: A Survey Analysis. JOJ Dermatol & Cosmet. 2024; 5(5): 555674. DOI: 10.19080/JOJDC.2024.05.555674
Abstract
Background: The current study survey aims to explore the impact of age groups and seasons on various skin types. A survey was performed by IncNut LifeStyle Pvt. Ltd., City, Country in 2021 and 2022. IncNut LifeStyle Pvt. Ltd. India is the 1st organization that designed customized products as per individual needs. To understand consumers’ actual needs over ‘wants’, the consumer needs to answer the questionnaire, which is about various attributes like skin type, gender, age, food habits, skin issues, etc. For skin type categorization, four options were provided i.e. Oily, Dry, Normal and Sensitive Skin. Data mapping and analysis have been done with the aid of proprietary validated software DiabloTM.
Result: The results obtained from the survey indicated the change in the pattern of various skin issues as per skin type viz dry; oil; normal; sensitive, and age groups as well as different seasons. Common skin issues were categorized as acne, pigmentation, anti-aging, and tan which are most observed. Survey outcome indicates that skin type, age, and season are important factors in determining common skin problems among individuals.
Conclusion: Therefore, the product formulated for such problems should be as per the needs of individuals, considering the above-mentioned factors like skin type, age group, and seasons, which will be beneficial for the consumer. IncNut LifeSyle Pvt. Ltd. and other such customization-based product manufacturers working on the root cause of the problem could bring a revolution in the cosmetic industry with a direct benefit to the end user of the product.
Keywords: Type of skin; Age; Season; Skin problems; Customization
Introduction
Human skin serves several important functions and is the largest organ in the body. It plays a role of barrier against external elements, regulates body temperature, and helps in the excretion of waste products. The condition of the skin can vary from person to person, and it is often classified into different types based on certain characteristics [1, 2]. Additionally, various skin problems can occur that may require attention and treatment. Skin is typically classified into four main types: normal, dry, oily, and sensitive. These classifications are based on factors such as sebum production, moisture levels, and sensitivity [2,3].
Normal Skin: Normal skin has a balanced sebum production, good moisture retention, and is generally free from major skin problems [2].
Dry Skin: Skin that is dry lacks proper moisture and feels tight, itchy, and rough. It may be caused by factors such as genetics, aging, weather conditions, or excessive use of harsh skincare products [1].
Oily Skin: As a result of excessive sebum production, oily skin looks shiny, has enlarged pores, and is prone to acne and other skin problems. Hormonal changes, genetics, and certain environmental factors can contribute to oily skin [4,5].
Sensitive skin: Skin is easily irritated, reacts to certain products or environmental factors, and may feel uncomfortable [5].
Skin Problems: Skin problems can occur irrespective of skin type and may be caused by various factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, seasonal factors, lifestyle choices, age, and certain medical conditions. Some common skin problems include [6-8].
Acne: In acne, pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and sometimes pustules form on the skin. It can occur due to excess sebum production, clogged pores, bacterial infection, or hormonal imbalances [6, 9, 10].
Pigmentation: Pigmentation refers to areas of skin that become darker than the surrounding skin due to increased melanin production. It can occur because of sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, or skin injuries including post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation [3,11,12].
Aging: As we age, the skin undergoes various changes, including the development of fine lines, wrinkles, sagging, and age spots. There are several factors that contribute to these changes, including genetics, exposure to the sun, and lifestyle choices.
Tan: The process of tanning occurs naturally when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such as from the sun or tanning beds. Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color, is produced when the skin is exposed to UV rays in order to protect the skin from UV radiation [13-15]. Age has a significant impact on the occurrence and severity of various skin problems. As we grow older, our skin undergoes several changes due to intrinsic factors (natural aging) and extrinsic factors (environmental and lifestyle factors). These changes can contribute to the development of different skin issues. Here are some common skin problems affected by age.
Wrinkles and Fine Lines: Aging leads to a gradual loss of collagen and elastin, which are responsible for skin elasticity. This results in the formation of wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging skin. Sun exposure, smoking, and other lifestyle factors can accelerate these effects [2, 16, 17].
Dryness: As we age, our skin tends to produce fewer natural oils, leading to increased dryness. Dry skin is more prone to irritation, itching, and flakiness.
Age Spots and Pigmentation: Accumulated sun exposure over the years can result in the development of age spots, also known as liver spots or sunspots. These are darker patches of pigmentation that appear on areas frequently exposed to the sun [17].
Skin Thinning: The epidermis (outermost layer of the skin) becomes thinner with age, making it more susceptible to damage and injuries. The skin may also heal slower due to reduced cell turnover and decreased blood flow [16, 17].
Skin Cancer: The sun’s harmful UV rays, as well as exposure to screens, increase the risk of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. People who are older tend to have accumulated sun damage, making them more susceptible to skin cancer [1, 18-20].
Age-related Acne: Some adults experience acne breakouts well into their 30s, 40s, and beyond. Hormonal changes, stress, medications, and other factors can contribute to the development of acne in older individuals [5, 21, 22]. Seasonal changes can have a significant impact on various skin problems. Different weather conditions and environmental factors can exacerbate or improve certain skin conditions. In this study, a comprehensive survey was made to explain the role of skin type, age, and season in various skin problems [15].
Methods
Using Diablo TM software from IncNut Lifestyle Pvt. Ltd. (City, Country), the survey data was analyzed over the period of 2021- 2022. In the survey, the consumers were asked to answer the questionnaire along with their details of sex, age, skin type, etc. The data was collected and subjected to statistical analysis (Diablo TM).
Result
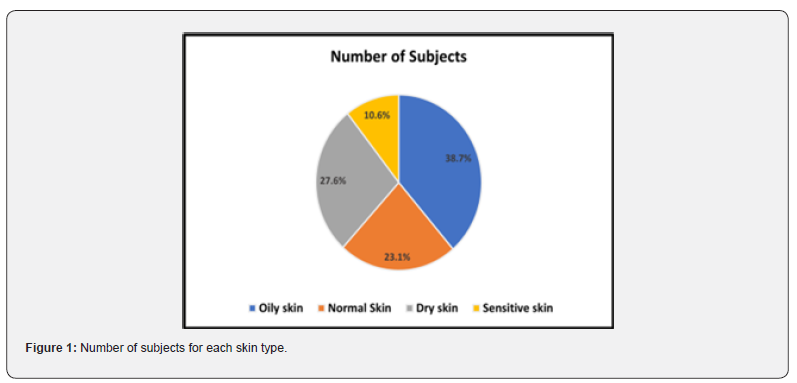
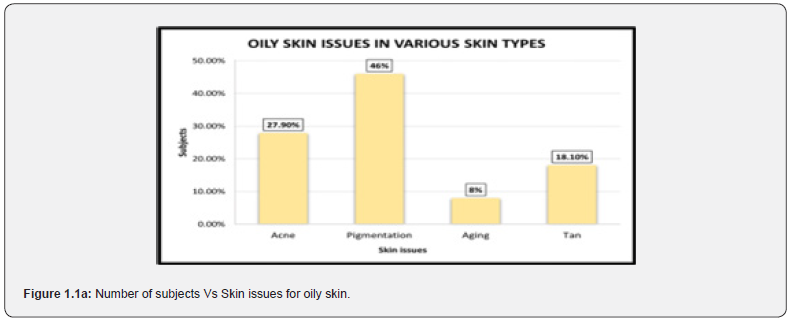
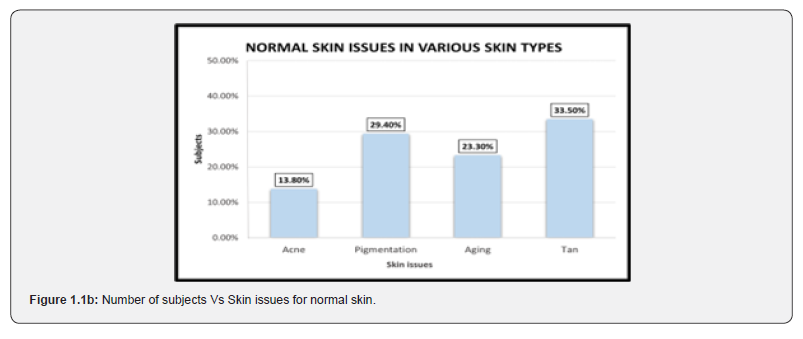
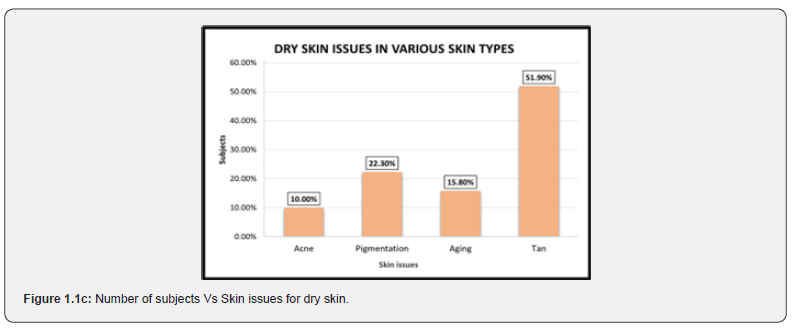
The response for various types of skin collected for two years included a total of 3,20,829 individuals. Of these total responses, 1,24,068 (38.7%) responded to oily skin, 74,095 (23.1%) exhibited normal skin, 88,623 (27.6%) with dry skin, and 34,043 (10.6%) responded to sensitive skin (Figure 1). Types of skin versus issues. It is evident from Figure 1.1a-d that people with oily skin face the highest problem of pigmentation (46%), normal skin has highest number of subjects with the problem of tanning (33.5%), dry skin was found with the problem of tanning (51.9%), and sensitive skin has the highest rate of pigmentation (27.8%) as well as acne (27%). Impact of age groups on various skin issues Age has a major contribution to the skin’s health. Different skin types in various age groups face skin issues in different ways. Data below shows how skin issue patterns differ with varying age groups for different skin types.
Oily skin
The age group 19-25 was found to be highly affected with skin problems such as pigmentation (67.2%), acne (49.6%), and tan (42.4%) in association to total acne and tan amongst all age groups. The problem of aging was at greater risk in the age group of 36-45 (36.7%) (The data is a comparison between all age groups and total responses received in all age groups concerning specific problems, considered to be 100%) (Figure 2.1).

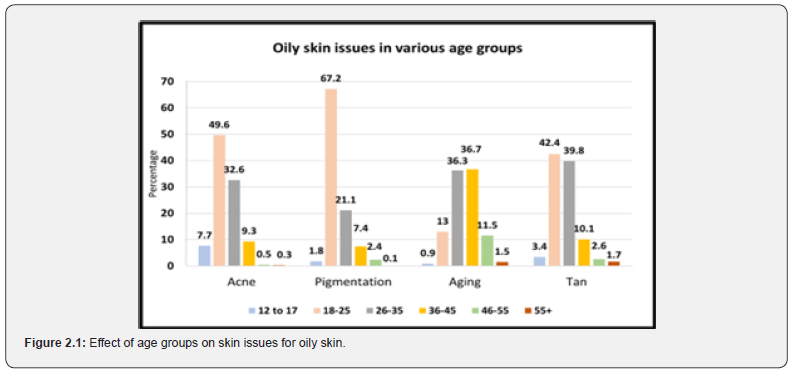
Normal skin
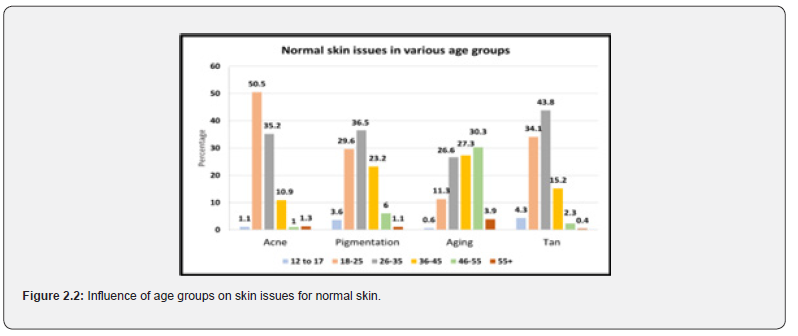
As depicted in Figure 2.2 acne was found to be elevated in the 19-25 age group (50.5%), tan (43.8%) as well as pigmentation (36.5%) was observed in the age group of 26-35. The age group 36-45 was with the highest number of aging (27.3%) issues (The data is a comparison between all age groups, total responses received in all age groups concerning specific problems is 100%).
Dry skin
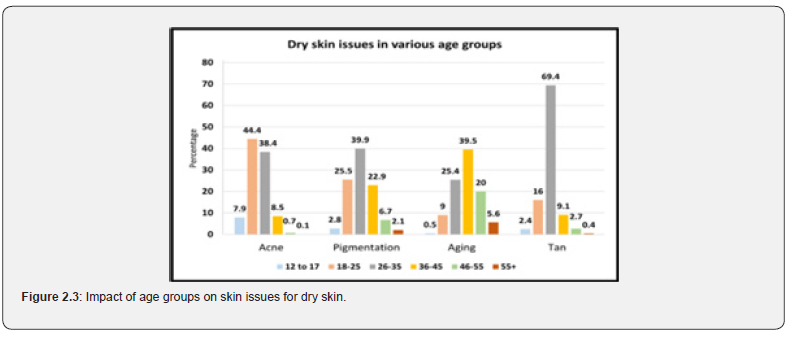
According to the study, the age group 26-35 was most affected with tan (69.4%), followed by pigmentation (39.9%), and acne was highest among 19-25-year-olds (44.4%). The problem of aging was highest amongst the age group 36-45 (39.5%) (The data is a comparison between all age groups, total responses received in all age groups concerning specific problems is 100%) (Figure 2.3).
Sensitive skin
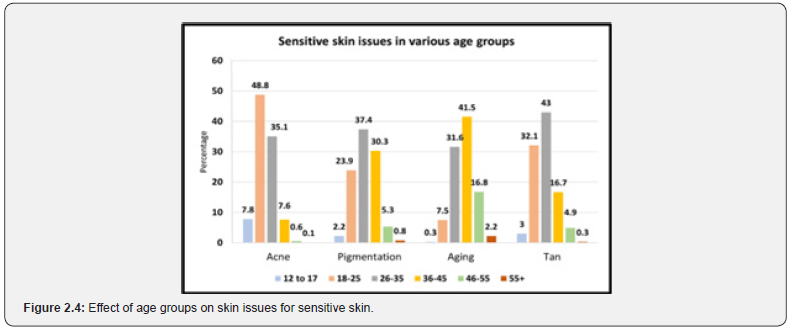
The age group 19-25 was observed with a major problem of acne (48.8%). Pigmentation (37.4%) and tan (43%) were slightly higher in the age group of 26-35. Aging was maximum in the age group of 36-45 (41.5%) (The data is a comparison between all age groups, total responses received in all age groups concerning specific problems is considered to be 100%) (Figure 2.4).
Influence of various seasons
Variations in skin health are influenced by seasonal changes. With changes in seasons, skincare should also be altered. The data below explains how various seasons affect skin issues. November 2021 to February 2022 months is covered as Winter season, March 2022 to June 2022 months is considered as summer season, and July 2022 to October 2022 are taken as monsoon season.
Oily skin
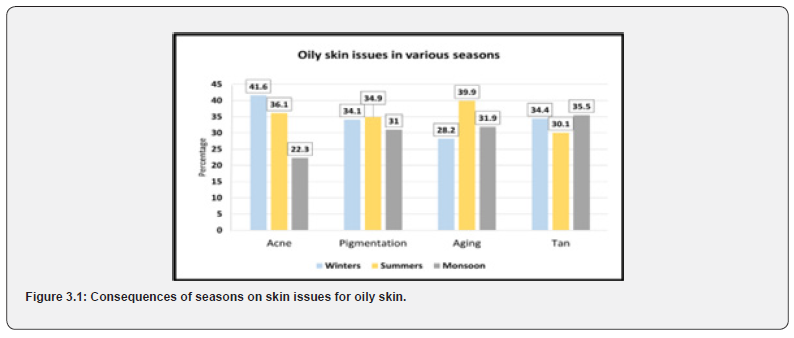
Individuals most commonly face acne issues in the winter season, with an estimated 41.6% of individuals affected. Pigmentation is the most prevalent in the summer season (March- June), with an estimated 34.9% of individuals affected. Further aging was the highest affected in summer, accounting for 39.9%, whereas tan peaks up during the monsoon season (Figure 3.1) (The data is a comparison between total responses received in a particular season concerning all skin problems is 100%).
Normal Skin
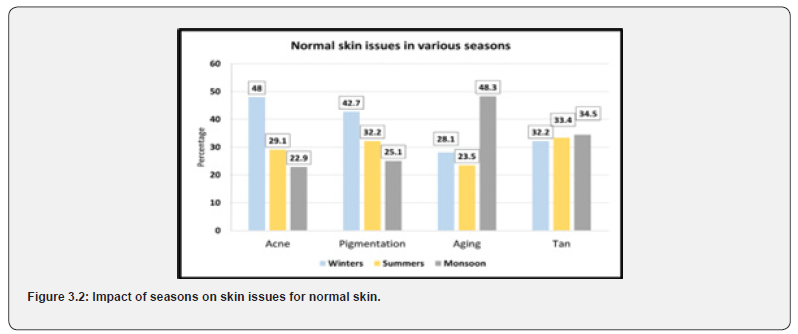
It was found that pigmentation was the problem for 36% of individuals in winter. Similarly in the summer season the responses showed the highest problem of tan (33.9%). The responses in monsoon season showed that the highest number of individuals were affected by aging (35.4%) (Figure 3.2).
Dry Skin
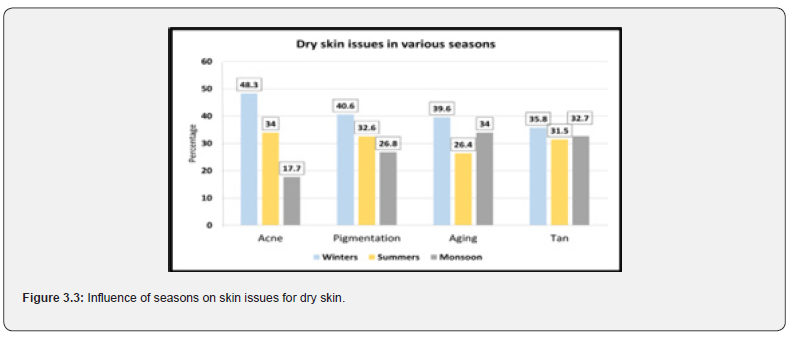
As per data provided in figure 3.3, it was evident that acne issues were highest in winter season with 48.3% of the total acne facing population. It was further observed that individuals with dry skin have the highest rate of pigmentation again during winters at 40.6%. Aging at 39.6% and tan at 35.8% are marked top in winters repeatedly. (The data is a comparison between total responses received in a particular season concerning all skin problems is 100%) (Figure 3.3).
Sensitive skin
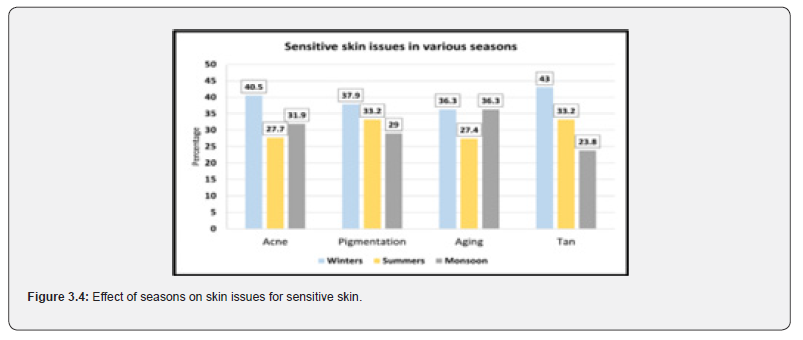
The responses in relation to sensitive skin exhibited the highest problem of acne at 40.5% (Figure 3.4) in winter. The same pattern is followed for other issues with pigmentation at 37.9%, then at 43% in winters. Whereas aging goes parallel at 36.3% during winters and monsoons (Figure 3.4).
Discussion
There are several common skin types, each with characteristics and potential problems. The potential problems commonly observed are acne, pigmentation, aging, and tanning. Moreover, age is one of the contributory factors in these skin types. According to age as well as type of skin the problems may differ amongst various individuals. Further, it was studied that seasons have an impact on skin issues as climatic conditions may alter the behavioral pattern of the skin [6,7,9,10]. In oily skin, seborrhea or seborrheic dermatitis, the sebaceous glands produce excess sebum, a natural oil. Despite its importance in moisturizing and protecting the skin, sebum can lead to oily skin when overproduced. Several factors contribute to the overproduction of sebum and the development of oily skin. The factors such as hormonal changes, genetics, environment (hot and humid stimulate sebum production), improper skin care, diet, and stress mainly contribute to oily skin. The results of the survey exhibited that the age group 19- 25 was highly affected with acne, pigmentation, and tan having oily skin. The age group 19-25 has numerous hormonal changes, an unhealthy diet; not having proper skin care with the recent scenario of stressful life and disturbed routine may be the possible reason for these types of skin problems [8, 23-25]. The age group 26-35 with normal skin, dry skin, and sensitive skin is commonly associated with pigmentation and tan. The reason for these skin problems occurs due to hormonal imbalance, sun exposure, and several environmental factors. The individuals in this group are mostly working and married. Pregnancy is usually preferred in this age which may lead to hormonal disturbances in females resulting in pigmentation. The exposure to sunlight along with the daily routine of working individuals results in pigmentation and tan. Aging is a natural process that occurs in living organisms over time. It involves a progressive decline in the body’s ability to repair and maintain itself, leading to physical and functional changes. While the exact age at which aging becomes noticeable can vary among individuals, the process typically becomes more apparent in middle age and beyond. It was found that aging was more above the age of 36. Aging is prominently developed with unhealthy lifestyles, lack of exercise, diet, and many more [24-27].
Different seasons can have varying effects on the skin, and certain skin problems may be more prevalent during specific times of the year. Oily skin tends to produce more sebum (oil) than normal or dry skin. This excess oil can clog pores and contribute to the formation of acne. In winter, the cold weather and low humidity can cause the skin to become dehydrated. In response, the sebaceous glands may produce even more oil to compensate for the lack of moisture, further exacerbating acne breakouts [5, 21, 24-28]. It was found that oily skin has major issues of pigmentation and aging during summer seasons. Excessive sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, and post-inflammatory responses can contribute to the development of hyperpigmentation. Oily skin can be more prone to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation due to the increased likelihood of acne or skin inflammation. While oily skin may show fewer visible signs of aging initially, it is still susceptible to the aging process. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle habits, and sun exposure can contribute to the formation of wrinkles, loss of elasticity, and other age-related concerns. As the monsoon season may bring cloudy or rainy days, it’s important to note that UV rays can still penetrate through clouds. People may not perceive the intensity of the sun due to the overcast weather, but UV radiation can still cause skin damage and tanning [1, 18-20, 22, 29].
Oily skin can sometimes be more prone to developing uneven or patchy tans due to the excess oil on the skin’s surface. The oil can act as a barrier, preventing an even distribution of sun exposure and leading to uneven tanning. Winter weather can lead to dry skin, even for those with normal skin. The cold air and low humidity can strip the skin of moisture, potentially causing dryness, flakiness, and an impaired skin barrier which leads to an increase in acne and pigmentation. The monsoon season is characterized by high humidity and increased moisture in the environment. These conditions can make the skin feel sticky and potentially lead to increased oiliness, especially in the T-zone area (forehead, nose, and chin), and potentially cause pigmentations as well as tanning. Dry skin can be particularly challenging during the winter season, as the cold weather and low humidity levels can exacerbate dryness and lead to various skin problems. Sebum production is low in dry skin, which compromises the skin barrier and makes it difficult to retain moisture. Cold weather and low humidity can strip its oil and cause skin problems. Hence it was observed that during the winter season acne, pigmentation, aging, and tanning are at the peak for dry skin in the winter season. Sensitive skin also behaves in a similar way to dry skin in winter leading to the development of the highest number of acnes, pigmentation, tan, and aging [30-33].
Overcoming skin problems requires a comprehensive approach that includes proper skincare, healthy lifestyle habits, and, in some cases, professional guidance and the right choice of cosmetic products. Determine your skin type (oily, dry, sensitive, or normal) and identify any specific skin concerns you may have (acne, pigmentation, etc.) [1,2,16,19,20,29,31,32]. This understanding will guide one in selecting appropriate skincare products and treatments. Getting enough sleep, managing stress levels, drinking plenty of water, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables, getting regular exercise, and getting regular exercise can all contribute to good skin health [3, 11-15, 33-35].
Conclusion
It can be concluded that everyone’s skin is unique, and individual variations exist within each skin type and age group. It’s important to observe your skin’s specific needs and adjust your skincare routine, accordingly, considering both your skin type, age, and the current season. As observed in the study the variations are characteristics concerning type of skin, age group, and season. Proper care should be taken in selecting the right type of skincare product. With Inc Nut Lifestyle Pvt Ltd City, consumers are provided with direct benefits based on their unique needs and problems. An expert team of dermatologists observes skin problems and determines the type of skin, age, and season, to provide the consumer with the most suitable skincare products. Further, this type of information could be a promising tool for the development of cosmetics according to an individual’s specific needs which will produce a greater rate of consumer satisfaction. Cosmetic manufacturers can work according to these problems to make their product better and consumer oriented.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate: As the study did not involve experiment on human/animal hence ethical approval was not applicable. The consent for participation was obtained from the customer in the form of their willingness to be part of conducted survey along with their personal details with the help of Diablo TM.
Acknowledgement
Authors are thankful to Incnut Lifestyle Pvt Ltd. Hyderabad India for providing infrastructure and facilities for carrying out present work. We are also thankful to all the participants who responded in the survey analysis.
References
- Li N, Yang XX, Yang RY, Yi F (2023) Study of the characteristics of facial skin tone status in 1092 young Chinese females according to the ITA°. J Cosmet Dermatol 21(5): 2073-2081.
- Oliveira R, Ferreira J, Azevedo LF, Almeida IF (2023) An Overview of Methods to Characterize Skin Type: Focus on Visual Rating Scales and Self-Report Instruments. Cosmet 10(1): 14.
- Zhang J, Wang Z, Shi Y, Xia L, Hu Y, et al. (2023) Protective effects of chlorogenic acid on growth, intestinal inflammation, hepatic antioxidant capacity, muscle development and skin color in channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus fed an oxidized fish oil diet. Fish & Shellfish Immunol 134: 108511.
- Seo JI, Ham HI, Baek JH, Shin MK (2022) An objective skin-type classification based on non-invasive biophysical parameters. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 36(3): 444-452.
- Hong JY, Park SJ, Seo SJ, Park KY (2020) Oily sensitive skin: A review of management options. J Cosmet Dermatol 19(5): 1016-1020.
- Cao L, Li X, Zhao J, Du Q, Dun J (2023) Skin pigmentation improvement with resveratrol microemulsion gel using polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil. Drug Dev Industrial Pharm 49(2): 207-216.
- CeraVe () What Type of Skin Do I Have?
- Cho SI, Kim D, Lee H, Um TT, Kim H (2023) Explore highly relevant questions in the Baumann skin type questionnaire through the digital skin analyzer: A retrospective single-center study in South Korea. J Cosmetic Dermatol 22(11): 3159-3167.
- Ali N, Zehra Z, Shamsi A, Beg MA, Parray ZA, et al. (2022) Elucidating the Role of Santalol as a Potent Inhibitor of Tyrosinase: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 27(24): 8915.
- Association AAoD (2018) How to Control Oily Skin.
- Zeitoun H, Michael-Jubeli R, El Khoury R, Baillet-Guffroy A, Tfayli A, Salameh D, et al. (2020) Skin lightening effect of natural extracts coming from Senegal botanical biodiversity. Int J Dermatol 59(2): 178-183.
- Zouboulis CC, Ganceviciene R, Liakou AI, Theodoridis A, Elewa R, et al. (2019) Aesthetic aspects of skin aging, prevention, and local treatment. Clin Dermatol 37(4): 365-372.
- Trezza BM, Apolinario D, De Oliveira RS, Busse AL, Gonçalves FL, et al. (2015) Environmental heat exposure and cognitive performance in older adults: a controlled trial. Age (Dord) 37(3): 9783.
- Wang YN, Fang H, Zhu WF (2009) Survey on skin aging status and related influential factors in Southeast China. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 10(1): 57-66.
- Yatagai T, Shimauchi T, Yamaguchi H, Sakabe J-i, Aoshima M, et al. (2018) Sensitive skin is highly frequent in extrinsic atopic dermatitis and correlates with disease severity markers but not necessarily with skin barrier impairment. Journal of Dermatological Sci 89(1): 33-39.
- Park BJ, Kim JE, Ko J, Kim MS, Park EJ, Lee GY, et al. (2019) Skin subtype categorization based on a new questionnaire for Korean women. J Cosmet and Laser Therap 21(1): 28-32.
- Passeron T, Zouboulis CC, Tan J, Andersen ML, Katta R, et al. (2021) Adult skin acute stress responses to short-term environmental and internal aggression from exposome factors. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 35(10): 1963-1975.
- Konarska A (2018) Microstructural and histochemical characteristics of Lycium barbarum L. fruits used in folk herbal medicine and as functional food. Protoplasma 255(6):1839-1854.
- Krishnaraj S, Mahadevappa K, Narayanaswamy RM, Kamnoore D, Lingutla R, et al. (2020) Development, Characterization and Pharmacological Evaluation of Antiblemish Cream Containing Herbal Oils. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul14(3): 223-232.
- Miyasaka K, Manse Y, Yoneda A, Takeda S, Shimizu N, et al. (2022) Anti-melanogenic effects of glucosylceramides and elasticamide derived from rice oil by-products in melanoma cells, melanocytes, and human skin. J Food Biochem 46(10): e14353.
- Jartarkar SR, Patil A, Wollina U, Gold MH, Stege H, et al. (2021) New diagnostic and imaging technologies in dermatology. J Cosmetic Dermatol 20(12): 3782-3787.
- Joseph N, Kumar GS, Nelliyanil M (2014) Skin diseases and conditions among students of a medical college in southern India. Indian Dermatol Online J 5(1): 19-24.
- Corazza M, Guarneri F, Montesi L, Toni G, Donelli I, et al. (2022) Proposal of a self-assessment questionnaire for the diagnosis of sensitive skin. J Cosmetic Dermatol 21(6): 2488-2496.
- Endly DC, Miller RA (2017) Oily Skin: A review of Treatment Options. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol 10(8): 49-55.
- Environ (2017) What's the difference between skin type and skin condition.
- Fayet-Moore F, Brock KE, Wright J, Ridges L, Small P, et al. (2019) Determinants of vitamin D status of healthy office workers in Sydney, Australia. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 189: 127-134.
- González-Cabrera M, Domínguez-Vidal A, Ayora-Cañada MJ (2021) Monitoring UV-accelerated alteration processes of paintings by means of hyperspectral micro-FTIR imaging and chemometrics. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 253: 119568.
- Gupta V, Sharma VK (2019) Skin typing: Fitzpatrick grading and others. Clin Dermatol 37(5): 430-436.
- Mohammed GF (2022) Topical Cyperus rotundus essential oil for treatment of axillary hyperpigmentation: a randomized, double-blind, active- and placebo-controlled study. Clin Exp Dermatol 47(3): 534-541.
- Alfredsson L, Armstrong BK, Butterfield DA, Chowdhury R, De Gruijl FR, et al. (2020) Insufficient Sun Exposure Has Become a Real Public Health Problem. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(14).
- Nakamura T, Yoshida H, Haneoka M, Nakamura S, Takahashi Y (2022) Season- and facial site-specific skin changes due to long-term mask wearing during the COVID-19 pandemic. Skin Res Technol 28(5): 749-758.
- Park EH, Jo DJ, Jeon HW, Na SJ (2023) Effects of winter indoor environment on the skin: Unveiling skin condition changes in Korea. Skin Res Technol 29(6): e13397.
- Silverberg JI (2019) Comorbidities and the impact of atopic dermatitis. Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol 123(2): 144-151.
- Shirshakova M, Morozova E, Sokolova D, Pervykh S, Smirnova L (2021) The effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A) in the treatment of facial skin oily seborrhea, enlarged pores, and symptom complex of post-acne. Int J Dermatol 60(10): 1232-1241.
- Ye C, Chen J, Yang S, Yi J, Chen H, et al. (2020) Skin sensitivity evaluation: What could impact the assessment results? J Cosmet Dermatol 19(5): 1231-1238.






























