Pigmented Condylomata Acuminata Seborrheic Keratoses -Like
Elharrouni Alaoui A1*, Douhi Z1, Mrabat S1, Elloudi S1, Baybay H1, Mernissi FZ1, Ennaciri S2, Ahsaini M², Mellas S², Tazi MF², El Amari J², El Fassi J², Farih MH²
1Departement of Dermatolgy, CHU Hassan II, Morocco
2Departement of Urology, CHU Hassan II, Morocco
Submission: January 07, 2020; Published: January 17, 2020
*Corresponding author: Elharrouni Alaoui A, Departement of Dermatolgy, CHU Hassan II, FEZ, Morocco
How to cite this article: Lemfadli Y, Jiddi S, Ait Errami A, Samlani Z, Oubaha S, Krati K. Myelomatous Ascites : A case report and Review of the Literature. 2020; 10(5): 555800. DOI: 10.19080/JOJCS.2020.10.555800.
Keywords: Condyloma acuminata Seborrheic keratoses Asymptomatic lesions Genital area Hepatitis B
Letter to the Editor
It is difficult to distinguish condyloma acuminatum from seborrheic keratoses (KS) and bowenoid papulosis when condyloma acuminatum exhibits pigmented lesions [1,2]. We here in report a case of a seborrheric keratosis -like pigmented tumor lesion of condyloma acuminatum in the pubic
A 32-years-old man, with no significant past medical history and a normal prior sex activity. He presented with a 4-year history of pigmented asymptomatic lesions in the genital area. The clinical examination revealed pigmented tumor and well demarcated plaque at the base of the sup pubic area, measuring 2 × 3cm with papillomatous surface. The dermoscopic examination showed crypts and brain-like appearance (Figure 1). There was no evidence of lymph node enlargement and the rest of the clinical examination was normal. The patient was deeply frustrated because of the absence of sexual intercourse with his wife since the manifestation of the lesions. The diagnosis of condyloma acuminata, basal cell carcinoma, melanoma and SK were evoked.An examination of human immunodeficiency virus, syphilis, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C proved negative. The patient was taken to shaving excision of the lesion under local anesthesia. The histopathological examination of the lesions showed revealed papillomatosis and acanthosis, a high-power view demonstrated a slightly the koilocyte with disordered arrangement of keratinocytes without atypia. Based on the clinical, dermoscopic and histopathological findings, a diagnosis of pigmented condyloma acuminata KS like was made. No recurrence was observed during a 3 - month follow-up.
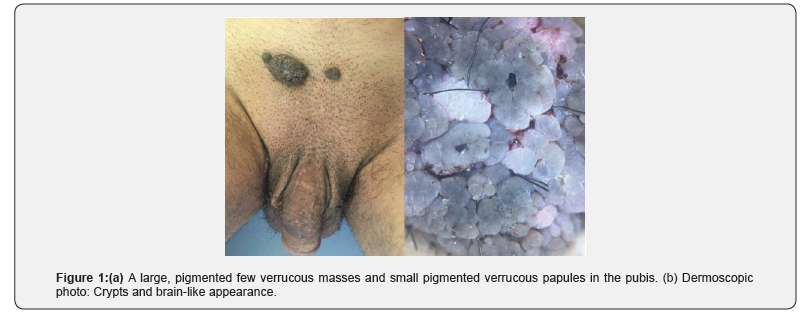
Condyloma acuminata (CA) is a benign tumor primarily caused by infection with HPV type-6 or type-11. CA may present with a variable clinical picture. Typical cases of CA can be easily diagnosed based on the clinical features alone [2]. Polypoid or verrucous lesions in the genitofemoral area may be harmless seborrheic keratoses or contagious condyloma acuminata [1]. A solitary lesion is particularly difficult to diagnose clinically, requiring pathological evaluation. The existence of pigmented papules of condylomata acuminata has been rarely described [3]. Herein we present a case of Pigmented condylomata acuminata with unusual clinical features in the inguinal area mimicking Giant Seborrheic Keratosis. In our case, the nodules on the mons pubis were similar to the pigmented papular lesions in CA. However, the pigmented tumor-type lesions seen in our patient have so far only rarely been mentioned in the published work [3].
References
- Chikandiwa A, Kelly H, Sawadogo B, Ngou J, Pisa PT, et al. (2018) Prevalence, incidence and correlates of low risk HPV infection and anogenital warts in a cohort of women living with HIV in Burkina Faso and South Africa. PLoS One 13(5): e0196018.
- von Krogh G, Lacey CJN, Gross G, Barrasso R, Schneider A (2000) European course on HPV associated pathology: guidelines for primary care physicians for the diagnosis and management of anogenital warts. Sex Transm Inf 76(3): 162-168.
- Kimura S (1980) Condylomata acuminata with pigmented papular lesions. Dermatologica 160(6): 390-397.






























