Healthy Diet on Early Adulthood Women
Rena Latifa* and Dick Hurry Maulana
Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, Indonesia
Submission: October 23, 2019;Published: October 30, 2019
*Corresponding author: Rena Latifa, Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, Indonesia
Rena Latifa, Dick Hurry Maulana. Healthy Diet on Early Adulthood Women. 2019: 17(2): 555956. DOI: 10.19080/JGWH.2019.17.555956
Abstract
A healthy diet is eating healthy or nutritious food, and doing physical activity that will improve stamina and maintain health. The purpose of this study was to determine whether social support (emotional support or appreciation, real support and instruments, informational support, and friendship support) and health belief model (perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, perceived barriers, cues to Action, and self-efficacy) can predict healthy diet behavior. Respondent are 314 early adulthood women who go on a diet (reducing the consumption of food, beverages that contain high calorie, high fat diet, and doing physical activity) at least for one month. Hypothesis test show the value Rsquare = 0.682, meaning that is the proportion of variance of healthy diet behavior described by all the independent variables by 68.2%. There are five variables that had a significant influence on healthy diet behavior that is emotional support or appreciation, support information, perceived severity, cues to action, and self-efficacy.
Keywords: Healthy diet behavior; Social support; Health belief mode
Introduction
Health is a fundamental aspect of human life. Health, according to WHO, can be interpreted as a healthy state of complete physical, mental, and social, and not merely a condition that is free from disease, disability and weaknesses [1]. Health is a basic and important thing for everyone, and unfortunately most people often forget about it. Usually when people fall ill, it is soon realized by the patient. Therefore, health care needs, will be a mandatory and required by the body. In everyday life, the actual intake of food, beverage, and nutrition absorbed by the body and physical activity such as exercise should be a major concern. Consuming good food, nutritious, and halal, will improve the stamina, so that the health could always be maintained.
Everyone wants to be healthy and want to have a fit body, as well as having an ideal body’s shape and weight. This is motivated by health reasons, as the person weight could affect a person’s appearance. Appearance and Health is something that is often arouse special attention, and every individual trying to make its appearance looks healthy and perfect in their social environment. It is very reasonable, considering one of the five basic human needs according to Maslow is the need for self-esteem/ self-respect. If the needs for self-respect and the respect of others is not met, the individual will feel helpless and feel inferior or insecure [2].
Young women are more likely to adopt the values were based on outward appearance. This is because at this age, a woman wants to always look attractive, and healthy in front of a friend, spouse or coworkers. In addition, people who are in their early adult phase would like to achieve closeness with others and trying to escape from aloofness [3]. Research conducted on 803 people in the United States, showed that, compared to men, women give more attention to health and their bodies [4]. Based on that idea, diet is one way that is effective and efficient to have or achieve a normal weight. Individuals are able to set the pattern of healthy eating habits (diet), will be able to maintain the stability of their weight properly so that they can be protected from obesity or overweight [5].
Diet is something that is very appealing on today. With an unlimited eating habit, plenty choices of delicious food, sometimes lead to obesity and make the body become less healthy. Many people vying to make their body slim and appear to be healthier. So far, women prefer a diet to lose weight and gain healthy. Kim and Lennon [6] explains that the diet includes behavioral patterns vary from the selection of food for good health until a very tight restrictions on the consumption of calories. According to Calhoun [7] in 1984, a market research company reported that 30% of American women and 16% of men go on a diet. National data in the US also stated that, approximately 44% of women trying to lose weight and the remaining approximately 26% of women trying to maintain their weight. Based on these data more than two-thirds of women, whose have a majority of normal body weight, they are all still actively control their weight [8].
One’s consciousness to maintain health are also characterized by self-limiting in food consumption. Researchers found that women who had a healthy diet and feel the benefits of a healthy diet will help her friends to have a healthy diet. So, does with the young women who go on a diet. Women in the age of 20-30 years old is dieting not only to beautify themselves but also to maintain the health [3].
Most women in their 30’s or older, have a diet to get back their shape. It is because at that age, usually women experience changes in their body shape. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), revealed that heart disease and stroke found among adolescents and early adulthood, because their habit of eating fast food. Not a few people with diseases such as heart disease and stroke is in their early adulthood, causing most women in early adulthood or in their 20’s-30’s begins to realize the levels of cholesterol or fat content in the food they consume.
In a report by the Weight Loss Plan [9], a few years ago, the adults may not have been all too aware of the existing cholesterol in their bodies, but now the adults began to realize how cholesterol affects their lives. Controlling cholesterol through diet and, if needed with drugs, can significantly reduce the risk of coronary heart disease [3]. Dietary adjustments in accordance with the rules and aiming to maintain health and achieve ideal body weight is called a healthy diet. A healthy diet can make a person have the ideal body, without incurring side effects that are harmful to the body.
Researchers revealed the successful and the effective strategies for losing weight is to eat less fat and doing more exercise. Participants from the National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey reported a weight loss of at least 5 percent of its original weight if they do a little fat diet and plenty of exercise and it will make a decrease of at least 10 percent of body weight when it is combined with a weight loss program [10]. In an experiment from 201 students who underwent weight control program, a combination of diet and exercise for 12 months, resulted in significant weight loss and improve the functions of breathing and the heart.
Women who have been successful on a diet usually continue to maintain their eating habit, even though their weight is already normal. They go on a diet in an effort to maintain a healthy body and protect them from diseases caused by unhealthy eating patterns. They go on a diet by adjusting the eating habit into a healthy diet and do more exercise. The problems that will arise later is the form of dietary behaviors chosen by women. The must to get the ideal body weight with a quick and easy process, will make women perform unhealthy diet, such as doing an unhealthy eating patterns, fasting excessively, exercising excessively, and et cetera.
As research conducted by Erdianto [11] on the deviation tendency of eating behavior in women at their early adulthood in the Social and Political Sciences Faculty of University of Indonesia said that, although the respondents have normal BMI, they still find themselves obese (38.8%). The feeling of having excessive fat perceived by the student as their body looks big (81.5%) and it does not look attractive. In addition, respondents also fear that their weight may up and become obese (28.7%). A total of 40.3% of respondents had a diet within the past one year. The reason is, most of the women doing dieting to prevent weight gain (85.2%) and their desire to have an attractive body shape (81.5%).
Dietary behavior committed by those who have a normal BMI and weight or even less, is feared will lead to insufficient nutritional intake that can affect their daily activities. The negative perception had by female students about the ideal body resulting in their obsessive efforts to control weight. Erdianto study [11] reported some ways to control body weight undertaken by the respondent is to reduce the frequency of meals (63%), reducing fat intake (59.3%), reducing the consumption of carbohydrates (55.6%), and exercising excessively (40.7%).
Research conducted by Hendrayati [12] revealed that 95.56% of respondents have an unhealthy diet with the category of unbalanced nutrition. The comparison between their BMI and nutrition showed that, 71.1% of respondents have a normal BMI but their intake is insufficient. While the results were alarming, that 17.78% of respondents fit into the category of thin body and they also have less intake.
Another study conducted by Ginting [13] in Noble (2010) showed that non medical students is still lacking in choosing their food menu, and failed to specify the time for a good meal, this statement is evident from the results of studies showing that only 12.9% choose the menu of good food category and 14.3% of non-medical students who choose a proper mealtimes in both category.
It is not easy for someone to decide having a proper diet, especially a healthy diet. Support such as the provision of information about a healthy diet, the provision of a healthy eating patterns as well as the appreciation for the selection of a healthy diet is necessary for someone who wants to run a healthy diet program. For that, they need social support from their environment. The survey from the International Food Information Council Foundation in 2011 stated that significantly, amounting to 36% of support from family and friends is a source of influence on improving healthy diet. Dieting means limiting carefully calorie consumption or certain foods, as long as it is done in proportion to the needs of the body, the diet can make the body lose weight and stay healthy. However, if it is done carelessly, it can be fatal. According to the survey from Horm and Anderson (2008) showed that 40% of women doing their weight reduction with unhealthy way. Many health experts blame the diet program that recently resulted in an increased incidence of anorexia or eating chronic failure, which resulted in half starved, and the occurrence of bulimia, trying to keep vomitting, fasting, or excessive abuse of laxatives [7].
A person with an unhealthy, or unbalanced eating patterns may not be on a diet. This is because the person does not receive social support in the form of information support of the consequences of the unhealthy diet. Social support can have beneficial effects on food choices and healthy diet changes (Devine, 2005). People who are in overweight state but have no awareness of their condition is very likely to not go on a diet. If it happens to a child, the social support as an instrumental support of the mother is very influential on changing their eating patterns behavior [14]. The instrumental support may include the provision of a healthy eating pattern to be consumed each day so that they can perform a healthy diet.
Other forms of social support are in the form of emotional support and giving special care or attention. Many people may go on a diet, but not many people are doing a healthy diet. Diet can be done by taking weight-loss drugs, but of course it is not a healthy one. Therefore it needs a special attention and concern from the closest person to the people who decide to go on a diet. Attention and cares from people nearby can predispose a person to a healthy diet. Someone will have a healthy diet when people around them give a sense of care to their behavior, the food they consume and the way they go on a diet. Social support from home and from fellow workers is positively associated with the improved fruit and vegetable consumption and the repair phase of eating habits consecutively [15].
Moreover, basically dieters need much supports, such as an appreciation when they go on a diet especially the healthy one. With the appreciation they got, it will affect the person to choose healthy diet than to buy drugs to get instant results. In relation to health behaviors, Rosenstock (1966) developed a model of how an individual’s belief predisposes a person to choose healthier behaviors. His theory is known as the health belief model or abbreviated as HBM. Health belief model of psychosocial approach is one of the most widely used to describe the behavior related to health. The main factor of this theory is the kinds of beliefs that is owned by an individual to influence their healthy behavior. By focusing on the belief or the individual assessment of his health, this theory organizes information about health and the factors that affect individuals in changing unhealthy behavior [16].
Health belief model (HBM) has long known as one of the most influential and the most popular model in the attempt to explain the behavior of health, both in preventing the onset of disease and in preventing the increase of the developed disease. This theory emphasizes the aspects of cognition that is often forgotten in studying the behavior of health [17].
This theory assumes that if a person is motivated to take healthy steps, the individuals need to be convinced personally that their health is susceptible to the disease (perceived susceptibility), and the disease is classified as serious (perceived severity). In addition, the perceived benefit is greater than the negative aspects (perceived barriers) obtained, when they put through healthy behaviors. Therefore, the assessment of who and what it makes itself moved (cues to action) to make healthy behavior, and the belief that they will succeed (self-efficacy) to perform the behavior is important. These four types of beliefs, cues to action, self-efficacy of HBM give more influence to an individual’s decision whether they would take steps to healthy behavior or not [16].
Research by Abood, Black and Feral [18] on “Nutrition Education Intervention for University Staff- Worksite Application of the benefits of health belief model”, reported that HBM especially, perceived, successfully used in the practice of healthy nutrition and nutritional knowledge associated with heart disease and cancer. Yunansih’s study [13] on the observance of type II diabetes mellitus patients, identified that high confidence in the perceived severity (level of perceived seriousness of the disease) give a strong impetus to act on a patient-abiding and purposeful suggestions by the doctor. thus the health beliefs helped identify the factors that influence health behavior, where one of the healthy behaviors is the behavior of the diet.
Based on the phenomenon and some research above, the researchers are interested in doing a study to find out whether social support (which consists of the dimensions of emotional support or appreciation, real support and instruments, support of information, and support of friendship) and the health belief model (perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, perceived barriers, cues to Action, and self-efficacy) can be a predictor of the behavior of a healthy diet at the early adulthood of women.
Research Methodology
In this study, a number of 314 female respondents in their 20’s to 30’s (early adulthood category; have a healthy diet for at least one month; where their activities of diets can be in the limitation of the consumption of foods and beverages that contain calories, high fat diet, and physical activity) selected as the research sample. Non-probability sampling techniques employed with the type of snowball sampling. Snowball sampling can identify the characteristics required by members of the same characteristics group (Henry, 1990).
Questionnaires used as the data collection. Researchers use three scales shaped models; Likert scale, health belief model, the social support scale, and the scale of dietary behaviors were prepared using four answer options, namely, strongly agree (SA), agree (A), disagree (D), and very disagree (VD). The scale used is the scale of health belief model [19] consisting of dimensions of perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, perceived barriers, cues to action and self-efficacy. Social support scale (Sarafino, 2011) consisting of dimensions: emotional support or appreciation, the real support or support of instrument, support of information, and support of friendship. Dietary behavior scale used in this study are based on weight loss behavior scale (WLBS) drawn up by the French, Perry, Leon and Fulkerson to then used as an indicator. Researchers only took 11 of the 23 weight loss strategy that existed at that scale, because it is already represented all the things that want to measure. The methods of weight loss or a healthy diet scale have reflects a healthy diet and exercise. This method consists of: a reduction in calories, exercising more, emphasis on eating fruits and vegetables, reduce cravings, reduce fat intake, reduce sweets or sugary foods, reduce food portions consumed, changes the type of food, reduce meat consumption, reduce carbohydrate foods, and consume foods in low calories. The analysis technique used is multiple regression analysis where the calculations are performed using SPSS 17.0 software.
Findings

Based on the results of R2 , it is 0.682, meaning the proportion of the variance of the behavior of a healthy diet, explained by emotional support or appreciation, real support or instrument, with the information and support of friendship, perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, perceived barriers, cues to action, and self-efficacy amounted to 68.2%, while 31.8% is influenced by other variables outside of this study Table 1.
The popularity test F on R2, obtained significantly for 0000 (sig <0.005), meaning that there was a significant effect of perceived susceptibility, perceived severity, perceived benefits, perceived barriers, cues to action, self-efficacy, emotional support or appreciation, real support or instruments, information support and friendship support to the dietary behavior. The F test results can be seen in Table 2 below.
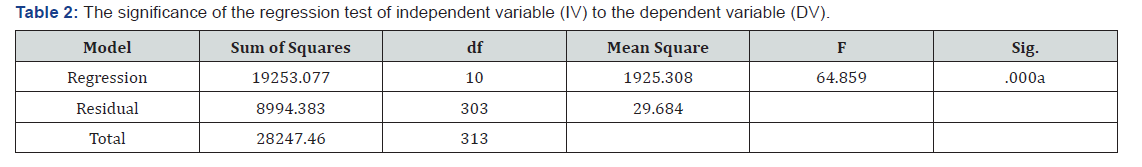
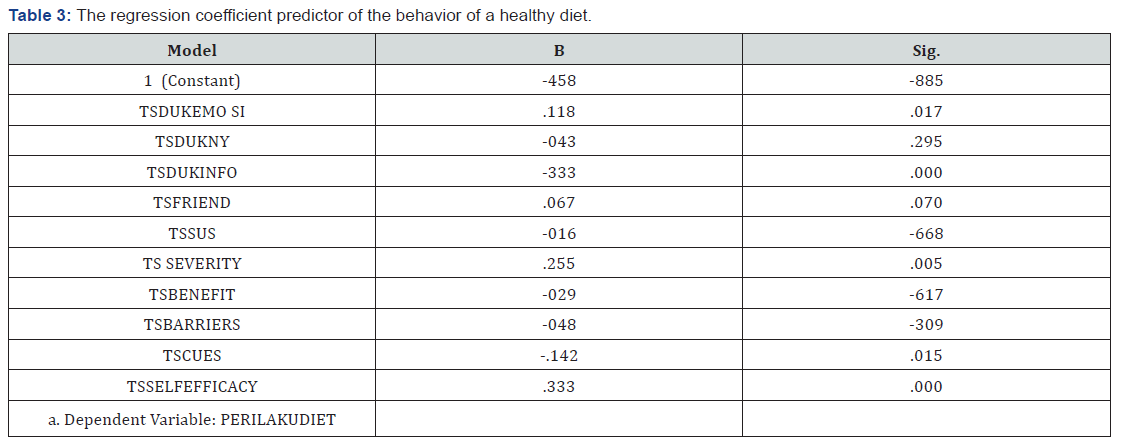
Based on the regression coefficients in Table 3, there are eight variables that significantly contribute to the behavior of a healthy diet that is emotional support or appreciation (β=0118), support information (β=0.333), perceived severity (β =0.255), cues to action (β =-0.142), self-efficacy (β =0.333).
Discussion and Recommendation
This study found a significant relationship between social support and healthy dietary behavior. This is according to research conducted by Wei Chang, et al [20] indicated that social support is one of the factors that influence dietary behavior, but the study only examined the overall social support so it has not reveal where the most significant dimensions is. In this research reported that emotional support or appreciation have an influence on the behavior of a healthy diet. This is in line with Vicki [21] where his research on cancer patients, said that the role of social support for cancer patients has an effect with their psychological adjustment. His research suggests that emotional support is the most desired by the patient. The results show that emotional support has a strong association with better adjustment in patients.
Support of information is also positively influence the behavior of a healthy diet, meaning that the higher the support information is, the higher the behavior of a healthy diet will be. This is consistent with research suggested by Thornton [22] in which the information support from husband is the most influential, important, and consistent support to the dietary behavior of a wife. Other studies [23] mention that the information media such as television becomes a role as a source of reference information in the search of healthy foods. From this study it is also found that a person who is undergoing a diet program, especially a healthy diet will be easier to run their diet when they are getting enough information support.
Furthermore, there is a significant influence between the health belief model of diet on behavior. This is according to research conducted by Robert (1997) which states that the health belief model is significantly influential in the reduction of stress in women before the wedding, and those who are doing dietary behavior. In another study by Abood, Black & Ferai [18] revealed that the health belief model significantly succeed used in the practice of nutrition and nutritional knowledge associated with heart disease and cancer. Other researchers [16] reported that with one focuses on the belief or judgment about health, it will affect them in changing behaviors related to one’s health.
The Dimension of health belief model that gives the most significant influence to predict the behavior of a healthy diet is the dimension of perceived severity. The higher the perceived severity owned by the people, the higher their healthy dietary behavior will be. The results of this study are supported by Sarafino [17] which states that individuals who believe the consequences of their health problems as a result of illness (perceived severity), such as the medical consequences (death, disability, and pain), psychological consequences (depression, anxiety and fear), as well as social consequences (impact on employment, family life and social relationships), the greater the confidence that the threat will be up to them. Confidence will be affected by the disease (perceived severity) and make the people motivated to make healthy dietary behaviors due to its many benefits and, it’s also a lifestyle that become a trend today
Another Dimension of health belief model that may influence significantly to predict the behavior of a healthy diet is the dimension of cues to action, where this dimension has a negative effect on the behavior of a healthy diet. This means that the higher the cues to action owned by a person, the lower their dietary behavior is. With more powerful cue or cues accumulation, a person is stimulated to take action. The more people feel the importance of assessing, or having bad omen for them, the lower the effort to do a healthy diet will be. This alert did not make a sign for people to change health behavior. Baranowski [23] ever found the results of research that prove most of the people do not feel the importance of assessing or getting bad sign for them to change their behavior. For example, their closest relatives died due to disease of obesity, but this case did not make them aware to change their health behavior.
The other dimension that significantly determines the behavior of a healthy diet is the dimension of self-efficacy. Self-efficacy describes an individual’s belief in their ability to make healthy dietary behavior. The higher self-efficacy on the individual the higher a person’s healthy dietary behavior will be. Self-efficacy has a strong relationship and significant impact on an individual’s effectiveness in performing a health program (Rita, 2012). A person is more likely to perform the behavior when they believe that they are able to do so. Self-efficacy is not only increasing the likelihood of individuals to adopt healthy behaviors but also reduces the inhibitory effect on the running behavior. Improving self-efficacy is the most effective way to reduce the perceived difficulties in the behavior of certain individuals [24-30].
The conclusion of this findings are: the behavior of a healthy diet in early adulthood women can be achieved in the presence of emotional support, information support, perceived severity, and self efficacy. Through emotional support, women feel being more welcomed and can make adjustments to choose a healthy diet. While going through the support of information she can find references for a healthy diet and positive effects of a healthy diet that has ever been experienced by others. A healthy diet will be easier to bear when people get enough information. The higher the perceived severity in a person the higher a person’s healthy dietary behavior will be. Confidence will be affected by the disease (perceived severity) and make people motivated to undergo healthy dietary behaviors due to its benefits and also it’s a lifestyle that is a trend today. The higher self-efficacy owned by a person the higher their healthy dietary behavior exists. Women are more likely to make healthy dietary behaviors if they believe that they are able to do so [31-37].
For further research, it can be examined the other types of healthy eating patterns such as mayo diet, water diet, and others diet in order to provide a comparison between each type of diet. Other researches also could study the behavior of a healthy diet in men, children, and adolescents. Regarding to the perceived severity, it may be advisable to early adulthood women who are doing the diet in order to increase their confidence to their healthy lifestyle and a belief that the disease could come over anytime. The seriousness of the danger of a medical illness that actually can be resolved as quickly as possible with early adjustment of diet, regular exercise, avoiding stress derived from work, family conflicts, and other social issues should be taken seriously.
References
- Abood DA, Black DR, Ferai D (2003) Nutrition education worksite intervention for university staff: Application of the Health belief model. J Nutr Educ Behav 35(5): 260-267.
- Alwisol (2009) Psikologi kepribadian edisi revisi. UMM Press, Malang, Indonesia.
- Andea R (2010) Hubungan antara body image dan perilaku diet pada remaja. Sumatera utara: Universitas Sumatera Utara,
- Ashton A, Lavers S, Haworth E, Helen L (2010) BTEC Level 2 first health and social care. Edexcel Foundation, London, UK.
- Belloc NB, Breslow L (1972) Relationship of physical health status and health p Prev Med 1(3): 409-421.
- Boyes AD, Fletcher GJO, Latner JD (2007) Risk factors for eating disorders: the role of intimate rJournal of Family Psychology 21: 764-768.
- Calhoun JF, Acocella JR (1995) Psikologi tentang penyesuaian dan hubungan kemanusiaan. Edisi Ketiga. Alih Bahasa: Satmoko RS, Edisi ke-3, Semarang: Ikip Semarang Press, Indonesia.
- Chang WM, Brown R, Nitzke S (2008) Scale development: factors affecting diet, exercise, and stress management (FADESM). BMC Public Health 8: 76.
- Cullen KW, Baranowski T, Rittenberry L, Olvera N (2000) Social-environmental indluences on children’s diets: results from focus group with african-, euro, and mexican american children and their p Health Educ Res 15(5): 581-590.
- Chaplin JP (2006) Kamus lengkap psikologi. (terj. Kartini Kartono 2006). Raja Grafindo Persada PT,
- Dariyo A (2004) Psikologi perkembangan dewasa muda. PT Grasindo, Jakarta,
- Eat more “Superfoods” to lose weight (2012) Diambil tanggal 15 Mei 2012 dari CNNHealth.
- Erdianto SD(2009) Hubungan antara faktor individu dan faktor lingkungan dengan kecenderungan penyimpangan perilaku makan pada mahasiswi jurusan administrasi perkantoran dan sekretaris FISIP UI tahun 2009. Skripsi FKM UI, Depok, Indonesia.
- French SA, Perry CL, Leon GR, Fulkerson JA (1995) Dieting behaviors and weight change history in female adolescents. Health Psychol 14(6): 548-
- Gillen MM, Charlotte NM, Patrick MM (2012) An examination of dieting behaviors among adults: Links with depression. Eat Behav 13(2): 88-93.
- Glanz K, Rimer BK, Viswanath K (2008) Health behavior and health education theory, research, and practice. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, USA.
- Helgeson VS, Cohen S (1996) Social support and adjustment to cancer: reconciling descriptive, correlational, and intervention r Health Psychol 15(2): 135-148.
- Hendrayati N (2007) Gambaran pola makan mahasiswa regular FIK UI. Laporan penelitian dibuat untuk memenuhi tugas akhir mata ajar riset keperawatan. Faculty of Nursing of Universitas, Indonesia.
- Ireland J (2010) Factors affecting a person’s diet. USA.
- Kim M, Lennon SJ (2006) Analysis of diet advertisement a cross-national comparison of Korean and U.S. women’s magazines. Clothing and Textiles Research 24:
- Latham B (2007) Sampling: what is it? quantitative research m ENGL 5377.
- Mulia A (2010) Pengetahuan gizi, pola makan dan status gizi mahasiswa Pendidikan Teknologi Kimia Industri (PTKI) Medan tahun 2010. Skripsi FKM USU, Medan, Indonesia.
- Orji R, Vassileva J, Mandryk R (2012) Towards an effective health interventions design: an extension of the health belief m Online J Public Health Inform 4(3).
- Papalia DE, Sally WO, Ruth DF (2009) Human development. McGraw-Hill, New York, USA.
- Perri GM, Kumanyika SK, Bowen D, Horn LV, Rolls BJ, et al. (2000) Maintenace of dietary behavior change. Health Psychol 19(1S): 42-56.
- Poppy K (1998) Kamus kedokteran dorland, copy editor edisi bahasa: Dyah Nuswantari. In: (25th Edn), Jakarta: EGC, Indonesia.
- Ruderman AJ (1986) Dietary Restraint: A theoritical and empical review. Psychol Bull 99(2): 247-262.
- Sarafino EP (2008) Health psychology biopsychosocial interactions. John Wiley & Sons, Inc,
- Sari DI (2008) Perilaku remaja puteri tentang diet sehat di SMU Dharmawangsa Medan. Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia.
- Schetter CD, Folkman S, Lazarus RS (1987) Correlates of social support receipt. J Pers Soc Psychol 53(1): 71-80.
- Smet B (1994) Psikologi kesehatan. PT Gramedia Widiasarana Indonesia,
- Smolak, L (1993) Adult development. Prentice-Hall, Inc, New Jersey, USA.
- Sorensen MV, Snodgrass JJ, Leonard WR (2005) Health consequences of postsocialist transition: dietary and lifestyle determinants of plasma lipids in Yakutia. Am J Hum Biol 17(5): 576-592.
- Taylor SE (2006) Health psychology. In: (6th edn). University California, Los Angeles, USA.
- Thornton PL, Kieffer CE, Young AO, Willis SK, Kim H, et al. (2006) Weight, diet, and physical activity related beliefs and practices among pregnant and postpartum latino women: the role of social s Matern Child Health J 10(1): 95-104.
- Yunansih (2002) Ketaatan penderita diabet tipe II terhadap saran-saran dokter ditinjau dari health belief model. Fakultas Psikologi Universitas Indonesia,
- Wood NL (2006) Understanding the construct of body image to include positive components: A mixed-methods study. The Ohio State University, USA.