Elder Abuse: A Forensic Odontologist's Perspective
Abraham Johnson*, Kushdeep Kumar Gupta, Dahiya and Dhwani Patel
Deportment of Forensic Science, Gujarat Forensic Sciences University, India
Submission: April 19, 2018;Published: May 10, 2018
*Corresponding author: Abraham Johnson, Assistant Professor, Institute of Forensic Science, Gujarat Forensic Sciences University, India, Email: drabrahamjohnson4000@yahoo.com
How to cite this article: Abraham Johnson, Kushdeep Kumar Gupta, Dahiya, Dhwani Patel. Elder Abuse: A Forensic Odontologist's Perspective. J Forensic Sci & Criminal Invest. 2018; 8(5): 555748. DOI: 10.19080/JFSCI.2018.08.555748
Abstract
According to the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007 a "Senior citizen” is any citizen of India who has attained 60 years and above whether living in India or not. Like everyone, even the elders have the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being of themselves, including food, clothing, housing and medical care, etc. But unfortunately elderly abuses are increasing as traditional joint family system are now transforming into small family system, with declining moral values and fast paced modern lifestyle. Elder abuse is any form of wrongful treatment by a person in a position of trust that leads in harm or loss to an older person.
A dentist is in an ideal position to recognize such suspected abuses, as they perform a thorough examination of the head and neck region and generally see their patients twice a year. Some of the findings seen in cases of elder abuse/neglect consist of physical trauma, poor hygiene, untreated or neglected medical conditions apart from dehydration, malnutrition etc. The dentist uses his or her clinical knowledge and experience to distinguish abuse from normal fragility of the tissues. This article gives a brief idea about the role of a forensic odontologist in cases of elder abuse and their rights. The forensic odontologist is regularly consulted when either law enforcement or health care personnel recognize that there is dental evidence connected to an incident.
Keywords: Elder abuse; Human Rights; Violence; Forensic; Forensic Odontologist
Introduction
In India, awareness about human right among elderly people is very low. India being a developed country in which the population of elderly population is more than young population. The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007 define senior citizens as the Indian citizens who have attained the age of 60 years or above [1]. Ageing is a natural process, which inevitably occurs in human life cycle. It brings with a host of challenges in the life of the old age, which is mostly engineered by the changes in their body, mind, thought process and the living patterns [2]. with the popularity of nuclear family, older people have become victim of elder abuse including, misbehave/mistreatment, restricted social life, abuse/mental torture, denial of basic needs, physical harassment/ assault, etc. Elder abuse, mistreatment and torture of older people are a manifestation of the timeless phenomenon of interpersonal violence in India. Being mistreated, verbally abused, and denied proper food, proper medication and care by younger members of family, older people are indeed in a very helpless situation [3].
According to United Kingdom's Action on Elder Abuse, "Elder abuse is a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person" [4]. Older people mainly face difficulties in the following key areas like Physical & Mental Health Community Care, social care, housing, transport, employment, income, education and leisure, safety &security,utilities & Consumer Protection, access to information and decision-making. The problems faced by the older age individuals mainly are economic problems, physical and physiological problems and psycho-social problems [3]. The main reasons of elder abuse include emotional and economic dependence on the abuser, changing ethos, lack of effective legal deterrents', increasing longevity and need for care of elder persons [5].
Forms of Abuse
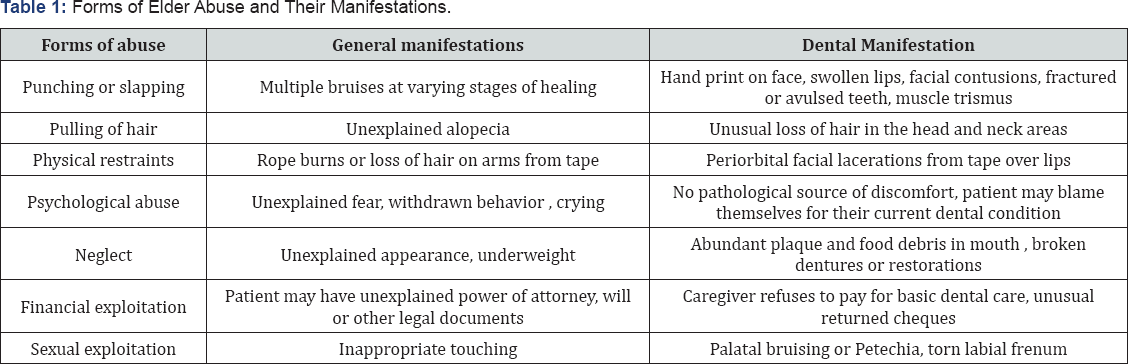
Abuse can take a variety of forms: physical, sexual, domestic psychological, financial, neglect ( Table 1)
Physical Abuse: is physical violence or force that results in bodily injury, pain, or impairment. It includes as battery, assault and inappropriate restraint. It mainly results in:
a. Fractures and dislocation of bones
b. Burns from hot iron rod, cigarettes
c. Shows marks of belt and ropes on arm, legs or torso
d. Internal injuries and abnormal functioning of organs.
e. Shows traumatic hair and tooth loss
f. Subdural hematoma was most common cause of death in victims of Physical abuse.
Sexual Abuse: Sexual abuse is any form of nonconsensual physical contact. It includes rape, molestation, or any sexual conduct with a person who lacks the mental capacity to exercise consent. It includes:
a. Irritation, pain or bleeding seen in genital or anal region.
b. Bruises seen on inner thighs and external surface of genitalia.
c. Difficulty walking or sitting.
d. Torn, stained, or bloody underclothing.
e. Sexually transmitted diseases.
Domestic Violence: Domestic violence it is a rising pattern of violence by an intimate partner, which is used to gain control and power. The following indicators are seen:
a. The injuries severity and frequency increases with time.
b. Victims often experience intense confusion and disassociation.
c. Violent incidents are often preceded by periods of intensifying tension and followed by periods of apparent contribution on the part of perpetrators
Psychological Abuse: Psychological abuse is the willful infliction of mental or emotional anguish by threat, humiliation, or other verbal or nonverbal conduct. Here, the perpetrator isolates the elder emotionally by not speaking to, touching, or comforting him or her. It leads to:
a. Significant loss or gain of weight
b. Rise in blood pressure
c. Insomnia
d. Shows confusion and depression.
e. Cowers in the presence of abuser.
f. Is emotionally upset, agitated, withdrawn, and non- responsive.
g. Disturbed unusual behavior attributed to dementia e.g. sucking, biting, rocking
Financial Abuse: Elder financial abuse include:
a. Captivating money or property
b. Faking an older person's signature
c. Getting an older person to sign a deed, will, or power of attorney
d. Using the older person's possessions or property without permission
e. Promising lifelong care in exchange for money or property and not following through on the promise
f. Dishonest acts or statements for financial gain as tickery and false pretence.
g. Telemarketing scams. Perpetrators call victims and use deception, scare tactics, or exaggerated claims to get them to send money. They may also make charges against victims' credit cards without authorization.
Neglect and Self- Neglect
Neglect is the failure of caregivers to fulfill their responsibilities to provide needed care."Active" neglect refers to behavior that is willful that is, the caregiver intentionally withholds care or necessities. The neglect may be motivated by financial gain (e.g. the guardian stands to inherit) or reflect interpersonal conflicts. "Passive" neglect refers to situations in which the caregiver is unable to fulfill his or her care giving responsibilities as a result of illness, stress, disability, ignorance, lack of maturity, or lack of resources. Self-neglect refersto things duringwhich there's no wrongdoer and neglect is that the results of the older person refusing care some of the indicators are:
a. Poor personal hygiene including soiled clothing, dirty nails and skin, matted or lice infested hair, odors, and the presence of feces or urine
b. Unclothed, or improperly clothed for weather
c. Bedsores
d. Skin rashes
e. Mental confusion, dehydration, dry sore mouth, dries fragile skin, apathy and lack of energy.
f. Untreated medical or mental conditions including infections, soiled bandages, and unattended fractures
g. Absence of needed dentures, eyeglasses, hearing aids, walkers, wheelchairs, braces, or commodes
h. Exacerbation of chronic diseases despite a care plan
i. Worsening dementia.
Prevalence of Abuse
According to a Case study in India, it has been found that 50% of the elders have experienced abuse personally while 83% of the elders reported that abusing is prevalent in the society. It is also noticed that 72% of the abused elderly people belong to the age group 60 - 69 years, 25% of them belong to the age group 70 - 79 and only 3% of them are of 80 years or above 80 with more prevalence in females than in males. In 2013, the ratio of personal experience of abusing was 23.10%. It shows that the condition of elders as the cases of abusing have increased rapidly in one year [6]. Every third elderly person (36.94% of overall affected elderly) stated misbehave/mistreatment as most common form of elder abuse, according to the survey by Age well Foundation. Restricted social life is ranked most common form of elder abuse [3].
Role of A Dental Health Professional
A dentist plays a major role in the identification of elder abuse, as they do examination of the head and neck region and see their patient twice a year [7]. As health care professionals our duty is to protect the safety of elders and elders’ right to selfdetermination, by treating elders with honesty, compassion and respect and giving care focusing on improving quality of life and reduce suffering. Some of the best practice guidelines include:
a. First do no harm
b. Interest of the senior is the priority
c. Avoid imposing your personal values
d. Respect diversity
e. Involve the senior in the plan of care
f. Recognize the senior's right to make choices
g. Use family and informal support
h. Recommend community-based services before institutional-based services, whenever possible
i. In the absence of known wishes, act in the best interests of the patient and use substituted judgment
Dentist may evaluate their parents on entry into the office by observing gait, appearance, communication skills and, of course, the head and neck region. Many patients visit their dentist every 6 months, whereas they visit their physician only yearly. Conversations with a suspected victim should be in a private area without any of the patient’s significant others present, and they should be witnessed by another staff member. Any physical evidence should be photographed and measured and its exact location documented. The dentist must always be aware of natural changes associated with aging such as thinning of the skin, increased potential for bruising due to systemic illnesses or medications such as blood thinners [8].
Role of Other Professionals
Other professionals can also be a great help in identification and rehabilitation of individuals suffered from elder abuse [9].
a. Physicians are in a position to diagnose and screen by undertaking medical component of multidisciplinary assessment, including physical examination, cognition, and mood. Once care plan is started, a proper follow-up and treatment becomes necessary.
b. Nurses are also in a position to identify such abuses as they are in more contact with patient during home care setting. When abuser is career, nurses are in unique position to provide support.
c. Social worker can coordinate for the medical and community response against abuse. Assists with situation- specific interventions (e.g., adult day care, respite services). Identifies family and new resources with which to offer plan of care.
d. Lawyers play a major role as they assist in guardianship proceedings, advanced care planning, and identification of surrogate decision makers. They can also assist in identification of resources to provide care and share the career's burden.
e. Law enforcement personnel should become an important part in gathering and presenting records and evidence.
Conclusion
With popularity of nuclear family, older persons have become victim of elder abuse including misbehave/mistreatment, restricted social life, denial of basic needs etc. Level of awareness about human rights in older persons is very low [3]. Problems of abuse among elder persons were more mental than physical. It was even more difficult to first, identify elder abuse and then tackle them. Senior citizen cells may be established in every district. Elderly helpline should effectively work. Police should give security to elder persons who are living alone. The bonding between the family members should be strengthened. Speedy, effective, efficient redress mechanism is needed to ensure the safe and happy life to elderly people. Pension schemes at various levels from government can be helpful to make them economic independent.
Elder abuses were instead presented to the doctors as major psychosomatic complaints that did not get cured with medicines. India is not lacking in law instead lacking in implementation of laws which is to be taken care of properly with appropriate measures. Dental health professional play a major role in identification of elder abuse during their patient treatment and their association with social workers and lawyers can be a help and support to elder abused victims.Apart from the political will in favor of the protection of old age people a strong and sensitive civil society is to be shaped so that the value based social responsibility of individual as well as of society at large can be created to prevent the pollution of our strong Indian Values where parents are consider as God in mortal form.
References
- (2014) Crime Against Senior citizen .
- ShashipNath Mandal (2011) Protection of Rights of Old age Person In India; A Challenging Facet Of Human Rights. Global Journal of Human Social Science 11(5):23-32.
- Human Rights of Older People in India.
- Silvia PL (2008) Discussing Screening for Elder Abuse at Primary Health Care level. WHO Press, World Health Organization, 20 Avenue Appia, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland.
- The National Committee for the Prevention of Elder Abuse (NCPEA).
- Punita G, Swati G (2016) Domestic Violence against Elderly People: A Case Study of India. Advances in Aging Research 5(5):110-121.
- Seniors Citizen Guide. Help Age India 2016.
- Wiseman (2008) The Role of the Dentist In Recognising Elder Abuse. JCDA 74(8):715-720.
- Mark S L, Karl P (2004) Elder abuse. Lancet 364: 1263-1272.






