Automated Tool Based on Statistical Study for Predicting Probable Dextrality of Writers
Kriti Nigam 1*, Vaibhav Saran2, Ankit Srivastava1, Syeed Ahmed3 and AK Gupta2
1Assistant Professor, Bundelkh and University, Jhansi, India
2Faculty, SHUATS, India
3SSO-I, DFSS, India
Submission: December 20, 2017; Published: January 08, 2018
*Corresponding author: Kriti Nigam, Assistant Professor, Bundelkh and University, Jhansi, India; Email: kritinigam1@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Kriti N, Vaibhav S, Ankit S, Syeed A, AK Gupta. Automated Tool Based on Statistical Study for Predicting Probable Dextrality of Writers. J Forensic Sci & Criminal Invest. 2018; 7(1): 555703.DOI10.19080/JFSCI.2018.07.555703
Abstract
Establishing handedness of writer in suspected document is a critical task and is often encountered by the Forensic Document Examiners. The present paper lays emphasis on estimating the probable dextrality of writers, based on statistical validation of features observed in 400 handwriting samples using chi square test. The frequency of features in samples was computed and relative probability was calculated. A computational tool is proposed here by using C++, which computes the input values given by user and suggests the probability of writer being dextral. The tool was validated by 50 unknown samples and found to be 89.14% accurate.
Keywords: Handwriting; Probable Dextrality; Automated Tool
Introduction
Handwriting is a highly complicated motor skill which involves together neurological, physiological and sensory impulses. Comprehension of form, acuity, visual perception, central nervous system pathways, and physiology and anatomy of the muscles and bones of the arm and hand are the factors which combine to generate the output as desired result [1,2]. Handwriting is affected by various internal and external features like handedness, gender, age, educational level of the writers. Classification of offline handwriting based on various attributes like handedness, age, gender and medium of education has a vital role in forensic document examination, it may help in minimizing the suspect list and hence the accuracy of positive identification in less time could be achieved. A similar classifier has been developed by Nigam et al. [3] for predicting the probability of female authorship.
Document experts rely on visual observation of handwriting features and sometimes their manual measurements, a computational approach which may measure the desired features of handwriting may assist the document expert in examination of document with higher accuracy level within less time consumption. Previous studies have reported many computational methods which are based on high level programming and personal models which are majorly based on optical character recognition, and no such classifier is proposed which may serve the document expert to categorize the handwriting into certain groups. Different character (microfeatures) have been found to be powerful for hand writing discrimination, however, their capability in identifying the attributes like gender, handedness, age, etc. has not yet been evaluated [4]. The present paper lays emphasis on estimating the probable dextrality of writers, based on statistical validation of features observed in 400 handwriting samples using chi square test.
Methodology
Handwriting samples of 400 writers (319 Dextrals and 81 Sinistrals) were randomly collected from different regions of Uttar Pradesh of age range between 18to 60 years without letting them know the purpose of the study. The participants were requested to copy the control passages in the unlined space of the same make of paper using the pen provided. They were requested to copy the passage for in handwriting specimen forms in their normal handwriting. The writings were preserved for further analysis. The digital image processing of the scanned handwritten samples were performed in several steps as followed:
Image Acquisition: The handwriting samples were acquired in a digital format by using High resolution HP LASERJET M1005 scanner at 1200 DPI and a dataset of 400 offline handwritings was prepared by compiling the scanned handwritten images and storing in memory of the system used.
Noise Removal: The noise appeared during image acquisition resulting from a number of factors, which affect the intensity of actual image, is removed using Range filters.
Image Segmentation: Noise free image is subjected to Otsu method for the segmentation of the pre processed image which chooses the threshold to minimize the intra class variance of black and white pixels [5].
Feature Selection: The image is further segmented to extract the features and the frequency of these features were statistically computed using chi square test and compared with the tabulated value to prove the alternate hypothesis that there is significant variation in dextral and sinistral handwriting as mentioned in Table 1. These features were then framed to use in the Program designed to calculate the probable dextrality of writer mentioned in Table 2 and (Figures 1A & 1B).
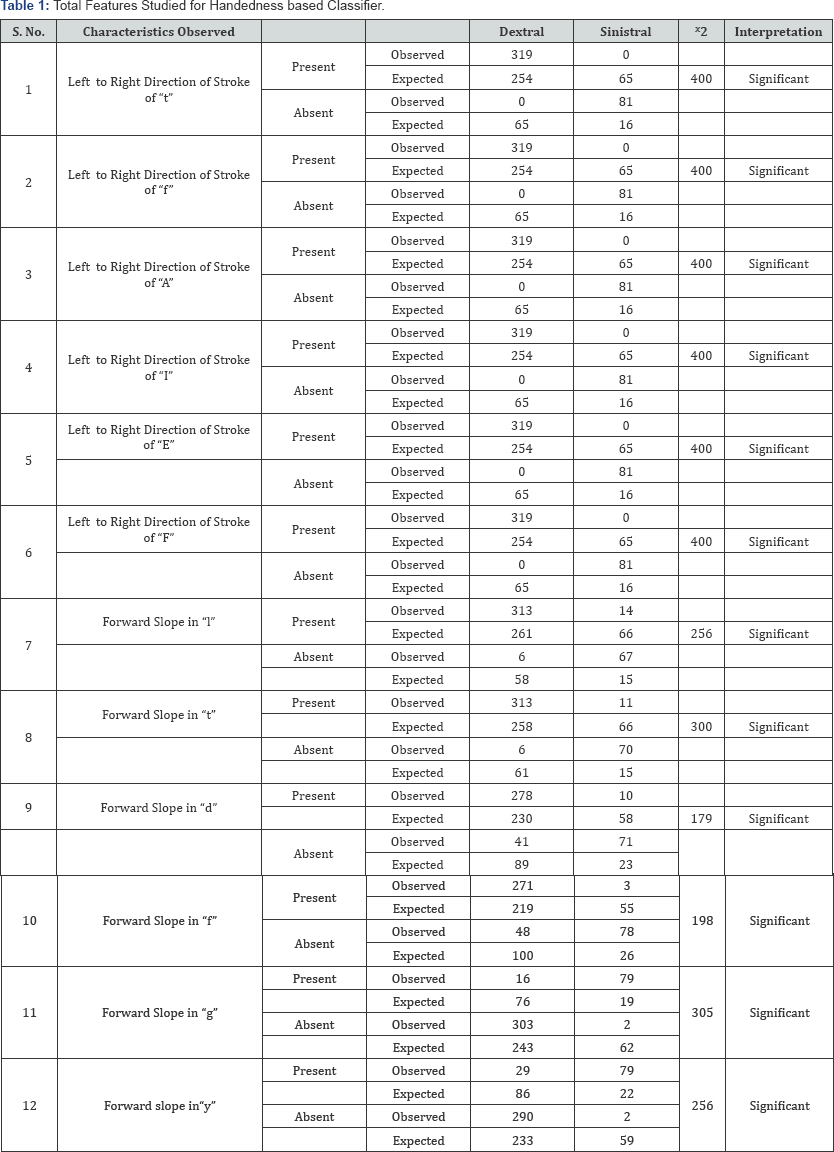
Note: At 5% degree of freedom, Ftab = 1.96

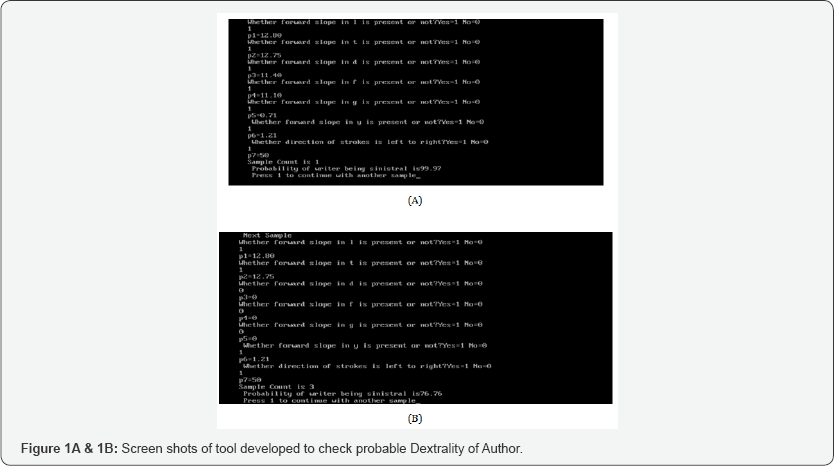
Result
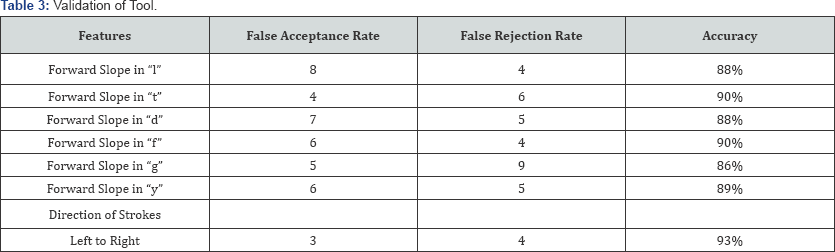
The proposed tool is based on the observation of features in handwriting samples, the examiner carefully examines the handwriting sample and enters the value 0 or 1 for the presence or absence of the features in that sample respectively. The tool then computes the values and displays the overall probability of the writer being dextral. The tool was formulated on statistical observation of 400 samples and them validated by 50 unknown samples. The False Acceptance rate (FAR) was highest in cases of forward slope in T 8% whereas the False Rejection Rate (FRR) was maximum in case forward slope in ‘g’ 9% as mentioned in Table 3. The tool has showed an accuracy of 89.14%.
Conclusion
The above mentioned features proved to be highly significant in differentiating the dextral writings. Along with this each feature is associated with its fixed probability value on the basis of their relative occurrence in the samples analyzed. Thus, a combination of different features will give a different probability of the handwriting being written by a dextral writer. The tool proposed in this paper will help the forensic document examiners to estimate the handedness of the writer of any anonymous document in a comparatively lesser period of time with greater accuracy.
References
- Huber RA, Headrick AM (1999) Handwriting Identification: Facts and Fundamentals. CRC Press-Taylor &Francis, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, p. 10-14.
- Hilton O (1982) Scientific Examination of Questioned Documents. Elsevier, New York, USA, pp. 153-157.
- Nigam K, Saran V, Ahmed S, Gupta AK (2013) Automated Tool Based on Statistical Study for Predicting Probability of Female Authorship. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology 2(11): 904-906.
- Srihari SN, Cha SH, Arora H, Lee S (2002) Individuality of handwriting. Journal of Forensic Sciences 47: 856-872.
- Saran V, Kumar S, Ahmed S, Gupta AK (2013) Computational method for forensic verification of offline signatures.IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering 14(2): 81-83.






























