Successful Bronchoscopic Removal of Aspirated Thumbtack in A Teenage Patient
Díaz Soriano S, Giannozzi L, Ruiz Tarbet CE, Pulido Hernández I, Ramos Manzano C and Rodrigo Garzón Manuel*
Pulmonology Service, Insular University Hospital, Las Palmas GC, Spain
Submission: February 15, 2025; Published: May 26, 2025
*Corresponding author: Manuel Rodrigo Garzón, Pulmonology Service, Insular University Hospital, Avenida Marítima s/n, Las Palmas GC, Spain
How to cite this article: Díaz Soriano S, Giannozzi L, Ruiz Tarbet CE, Pulido Hernández I, Ramos MC, et al. Successful Bronchoscopic Removal of Aspirated Thumbtack in A Teenage Patient. Int J Pul & Res Sci. 2025; 7(5): 555724.DOI: 10.19080/IJOPRS.2025.07.555724
Abstract
Keywords:Foreign body; Thumbtack; Respiratory symptoms; Bronchoscopy; Diagnosis
Introduction
Adults and children foreign-body aspiration often result in proximal airway obstruction and acute life-threatening asphyxia, but in some cases, the foreign body may remain inside the airways for an extended period before causing any respiratory symptoms [1,2]. In this report, we discuss the diagnostic and therapeutic approach to this clinical presentation.
Clinical Case
We introduce the case of a 17-year-old male who presented with suspected aspiration of a foreign body, later confirmed to be a thumbtack.
Case Details
Case Details
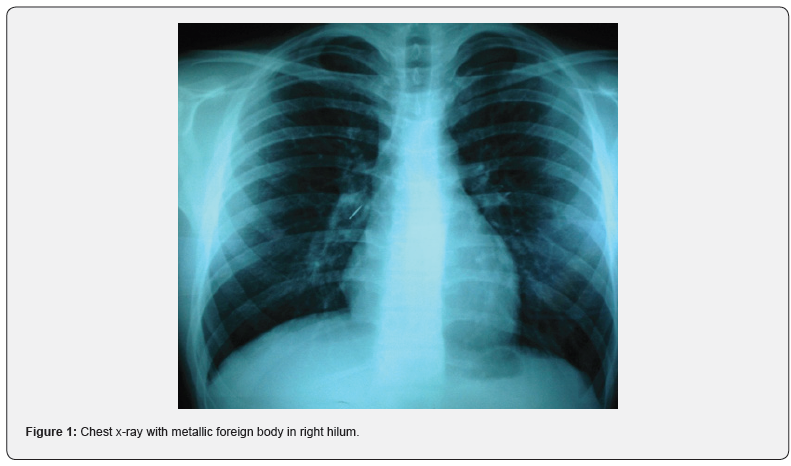
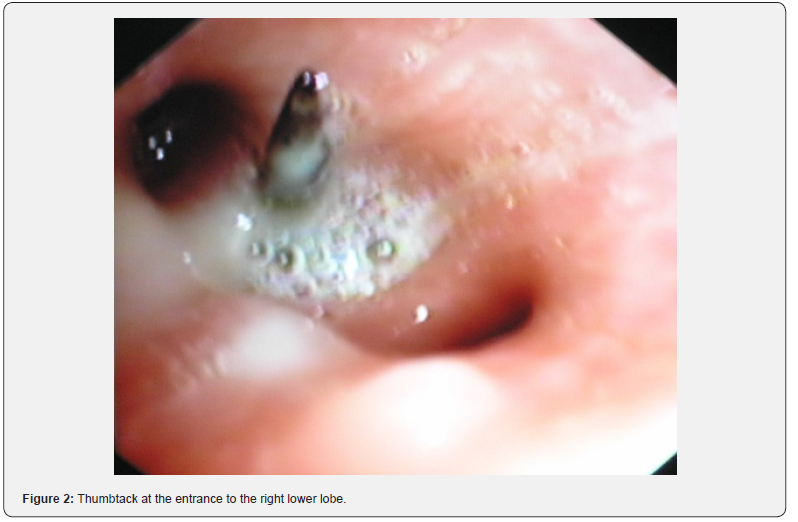
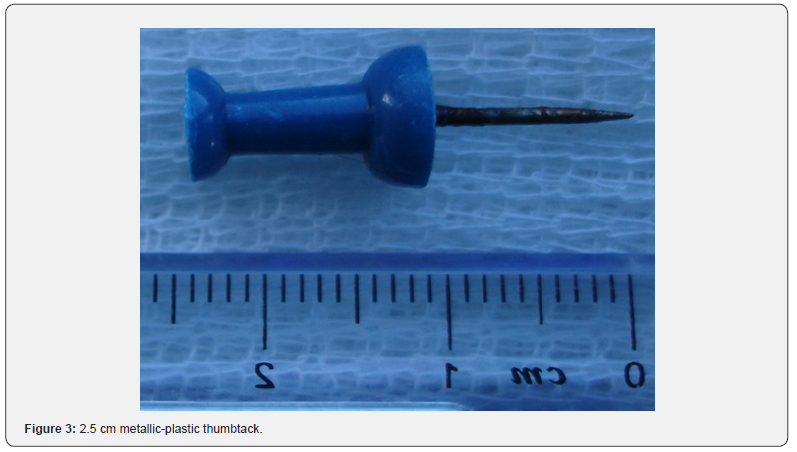
A 17-year-old male with no significant medical history presented to the emergency department with a complaint of a foreign body aspiration. He was playing with a thumbtack in his mouth when he sneezed. With the quick inhalation prior to the sneeze, the aspiration of the foreign body occurred. The patient only reported some cough and all vital signs were stable. A chest x-ray was performed which revealed the presence of a metallic foreign body in the right hilum (Figure 1). An urgent videobronchoscopy was performed that confirmed the presence of a metallic foreign body compatible with a thumbtack lodged at the entrance of the lower right lobe (Figure 2). The foreign body was extracted on the third attempt with a grasping forceps, revealing a 2.5 cm metallic-plastic thumbtack (Figure 3). Distal bronchial patency was confirmed after the extraction. The patient was discharged the same day without any complications during follow-up.
Discussion
Foreign body aspiration is a common occurrence, especially in children and certain adults population, but it can happen to anyone. It can lead to severe complications requiring prompt intervention, but in some cases, the diagnosis may be delayed as patients may not have a clear history of aspiration or may be asymptomatic initially [1,2]. In this case, the patient was perfectly aware of the aspiration which facilitated early recognition and management. Its extraction can be complicated by factors such as the nature of the aspirated object [3]. Thumbtack aspiration, in particular, is a unique challenge due to the sharp nature of the object, which can become entrapped during extraction.
Conclusion
Flexible bronchoscopy is the preferred method for foreign body retrieval; the use of rigid bronchoscopy is reserved in case of failure in extraction with the flexible instrument or in pediatric population [3-5]. We describe the successful management of this difficult foreign body to extract with the help of flexible bronchoscopy and forceps.
Conflict of Interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest no source of funding.
References
- White JJ, Cambron JD, Gottlieb M, Long B (2023) Evaluation and management of airways foreign bodies in the Emergency Department Setting. J Emerg Med 64(2): 145-155.
- Kara K, Ozdemir C, Tural OS, Satici C, Tokgoz AF, et al. (2004) Late diagnosis of foreign body aspiration in adults: case series and review of the literature. Respir Care 69(3): 317-324.
- Erik, Folch and Majid, Adnan (2013) Bronchoscopy for foreign body removal. Mehta, AC and Jain P Editors. In Interventional Bronchocopy, Editorial Human Press, pp. 227-243.
- Safia A, Abd Elhadi U, Bader R, Khater A, Karam M, et al. (2024) Flexible versus rigid bronchoscopy for tracheobronchial foreign body removal in children: a comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med 13(18): 5652.
- Bajaj D, Sachdeva A, Deepak D (2021) Foreign body aspiration. J Thorar Dis 13(8): 5159-5175.






























