- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
A Novel Revolutionary Approach of a Synthesis and Application of Targeted Nanosponge Drug Delivery
Parag Raj Behura1* and Vamshi Krishna T
Department of Pharmaceutics, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, India
Submission: May 27, 2021; Published: June 28, 2021
*Corresponding author: Parag Raj Behura, Department of Pharmaceutics, Specialization Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Karnataka, India
How to cite this article:Parag R B, Vamshi K T. A Novel Revolutionary Approach of a Synthesis and Application of Targeted Nanosponge Drug Delivery . Glob J Pharmaceu Sci. 2021; 8(4): 555743. DOI: 10.19080/GJPPS.2021.08.555743.
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Abstract
The novel and development of nanotechnology have brought a term targeted drug delivery system. Targeting a molecule to a specific site has brought a certain pharmacological action. Nanosponge is a part of nanotechnology which is both hydrophilic and lipophilic in nature. They are colloidal carriers which improve the aqueous solubility of the poorly soluble drug by enhancing and improving the physical and chemical stability and improving the permeability and bioavailability in the body tissues. Nanosponge are tiny sponges which are in the size of colloidal sizes and nanosized cavity. There general application can be seen in oral administration, parenteral administration, topical administration and available in the form of hydrogel. The current review discussion various methods of synthesis and application of nanosponges.
Keywords: Nanosponge; Hydrophilic; Lipophilic; Aqueous solubility; Route of administrationm
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
A Nanosponge Synthesis and application can determine the helpful outcome of treatment of several Cancer therapies, Breast cancer, inflammation, Brain tumor, Antifungal therapy, and treating poison in blood as adsorbent. Generally, it is difficult to understand the chemistry behind the targeted drug delivery system. Whether how much drug dose to be given and to prevent overdose [1,2]. So, a new term “Nanosponge” is introduced where it is the resulting combination of the Polymer and crosslinker. It has a size of about 50nm or less than that. They can withstand a temperature of about 300 degrees high temperature. They encapsulate the molecular drug which is lipophilic in nature by engulfing it within its core when it covers the molecular drug it forms a hydrophilic covering open structure like a membrane [3,4]. For example, Nanosponge likes Sodium alginate Poly-L-Lysine where it encapsulates the Antisense oligonucleotides drug molecule within its core and releases the drug for cancer therapy viral infection pathological-disorders. This type of study is used for Pharmacokinetic satisfaction on an in-vitro in vivo model called mice. Nanosponges are nano solid in form and can be formulated in the form of oral, Parenteral, or inhalational dosage forms. For oral administration, these are prepared in a mixture of excipients. Which is compressed on either tablet. For Parenteral administration, these are easily mixed with saline and other aqueous solutions. For Topical dosage form, Nanosponge can be effectively incorporated into the topical hydrogel.
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
When the Nanosponge-based formulation (Polymer +Crosslinker) in the encapsulated-based form. These can be either in the form of injection or Cream or lotions applied on the skin. It gets penetrated through the minute skin pore cavities leading to reach the carrier the Blood flowing RBCs which tends to bind it to RBCs cellular component. thereby reaching the desired targeting cell by giving almost Pharmacological action.
Advantages
a) the drug encapsulated nanosponge provides a pharmacological action to the targeted site delivery system [5-10].
b) It is non-toxic and non-mutagenic.
c) It can reduce the irritation without reducing the efficacy.
d) It can mask the unpleasant flavor of the drug.
e) It tends to improve the stability, flexibility, and elegance of the formulation.
Disadvantages
a) During loading of nanosponge it depends [11,12] mainly on the degree of crystalline. P-crystalline nanosponge shows different loading capacities.
b) Since it is tiny molecule chances of dose dumping is possible.
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
Stage 1: which is also known as the “Plain Nanosponges” includes functional group-based cyclodextrin nanosponges which are connected to crosslinker [13].
a) Cyclodextrin-based carbamate nanosponges
Eg: Crosslinkers like Disocyanate encapsulate the drug generally steroids. It is prepared with the help of solvent-based synthesis [14].
b) Cyclodextrin-based Ester nanosponges
Eg: Crosslinkers like Anhydride encapsulates the drug Ibuprofen. It is also prepared with the help of Solvent-based synthesis [15].
c) Cyclodextrin-based Carbonate nanosponges
Eg: Crosslinkers like Carbonyl encapsulates the drug itraconazole which is prepared with help of either the Solvent extraction method or thermal desorption method [16].
Cyclodextrin-based Ether nanosponges
Eg: Crosslinkers like Epichlorohydrate encapsulate the drug captopril which is prepared by the method Solvent-based synthesis [17].
Stage 2: which is also known as the “Modified nanosponges” are categorized on the basis of specific properties. Such as fluorescence and electric charge Eg: Crosslinker like carboxylated nanosponges encapsulates the drug Antiviral agent Acyclovir [18].
Stage 3: Which is also known as the “stimuli-responsive nanosponges”. They are categorized by external changes in the environment such as temperature, Redox condition, and pH Eg: Glutathione bioresponsive cyclodextrin nanosponges [19,20].
Stage 4: This is also known as the “Molecularly imprinted nanosponges “ which is categorized on the basis of the high selectivity of specific molecules. Eg: Biomimetic estimation of glucose using molecular and molecular imprinted polymer nanosponges [21].
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
Melt-based synthesis
This type of technique involves melting up of a combination. Crosslinking agents with cyclodextrin where it’s mixed at a maximum speed with the help of a magnetic stirrer at a very high temperature where the fusion of both cyclodextrin and the crosslinking agent takes place. This technique is also called as fusion method. The mixture is left for cooling and washing is done to remove the unreacted substrates [22].
Solvent-based synthesis
This technique involves only solvents, where a polar solvent like Dimethylsulfoxide or dimethylformamide (DMSO/DMF). Finally, crosslinker like carbonyl-based nanosponges is added in the ratio of 1:4. The reaction was maintained at a temperature of 10 degrees celsius for refluxing time for about 1-48hr. Once the solution temperature is settled down to 30-degree celsius and the demineralized water is added to remove the unreacted product and thereby product is filtered under vacuum. The final product is purified with the help of the soxhlet apparatus by the addition of ethanol to it. Later after a certain longer period of time of purification. The final product is subjected to drying [23].
Microwave-assisted synthesis
It is the simplest method compared to melt-based synthesis. where this technique exhibits the four-time reduction in the reaction time. It makes the nanosponges property a higher degree of crystallization and shows homogenous distribution with the polymer [24].
Ultrasound-assisted synthesis
This technique involves Ester-based cyclodextrin and Diphenyl carbonate are taken together and put in a vial. Then the vial is kept in an ultrasound bath consisting of water in it and heated at a temperature of 90 degrees celsius and sonicated for about 5 hr. Further purification and crystallization are done by washing it with Demineralized water to remove the unreacted product. The final product is filtered with the help of a vacuum, and it is further purified and dried with the help of soxhlet apparatus consisting of ethanol [25].
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Application of Nanosponges
Molecular drug targeting
In one of the articles it is claimed that the GSH-responsive cyclodextrin-based nanosponge encapsulated the drug doxorubicin showed therapeutic action and efficacy in human Hep G2 cells (in-vitro) and organotypic cultures of rat precisioncut liver slices (PCLs, ex-vivo) [26].
As toxin therapy
Polymeric nanosponge tends to absorb the membrane damaging toxins which leads to a diversion away from cellular targets (In-vivo study) in mouse, the nanosponge tends to heal the toxicity of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin (α-toxin) which can increase the survival capacity of the toxin of mice [27] (Figure 1-4).
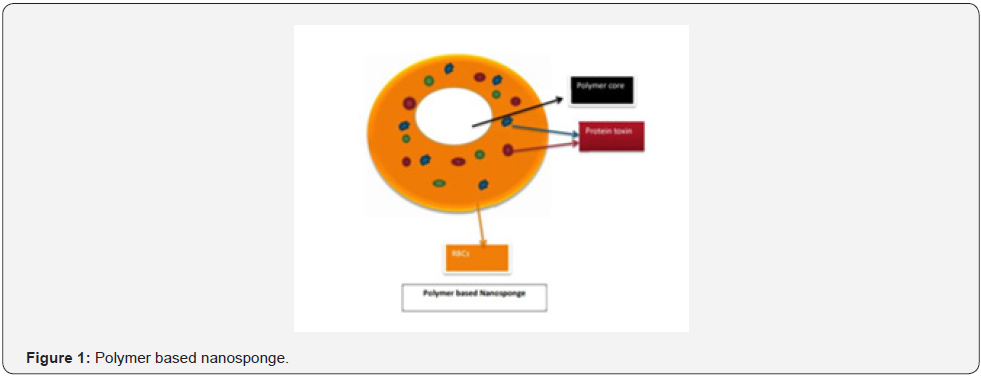
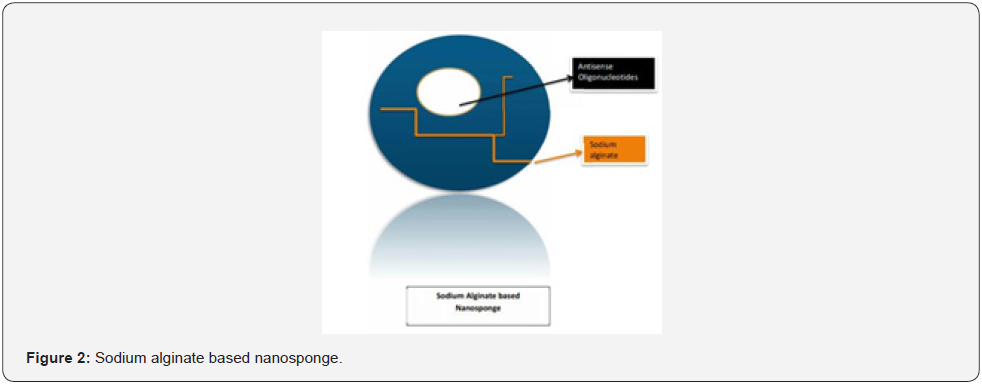
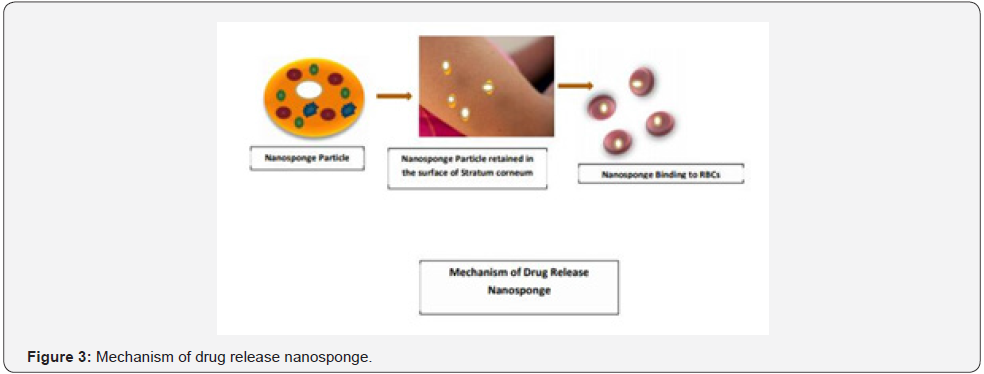
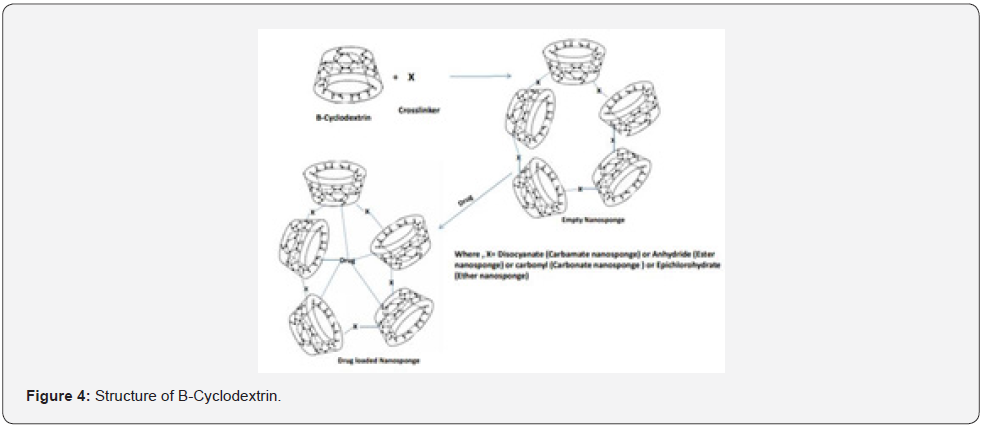
As dermal penetration
In the case of skin absorption cyclodextrin is crosslinked with the pyromellitic dianhydride which tends to give a semisolid formulation that is applied on the skin. Diclofenac is an antiinflammatory drug. which is typically formulated as an ointment form because of its composition. It is able to penetrate the dermal skin. This cyclodextrin nanosponge does not affect during penetration of diclofenac into the skin. But diclofenac dose can be controlled by the addition of pyromellitic dianhydride [28].
As an anticancer therapy
A major challenging nowadays drug. which are used in the treatment of cancer because of their low solubility and low permeability one such example is paclitaxel anticancer drug which belongs to BCS IV (Biopharmaceutical classification system) where carbonyldiimidazolebased cyclodextrin nanosponge encapsulate the drug paclitaxel and take it to the desired targeted cell to show its pharmacological action [29].
For Raman Spectroscopy
In recent study which were introduced by Occon optics. The newly equipped RAM-SERS-SP surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Subtrates tend to use a proprietary gold-silver nanosponge alloy to produce highly sensitive tracing capacity of Raman spectroscopy which in turn helps in detection of explosives, food safety, narcotics and biological research. Here, silver only SERS substrates work with best with 532nm gold. Substrates are better suited to 785nm. Both silver gold only SERS substrates combined work with 638nm raman excitation [30].
Oxygen delivery system
Three types of Cyclodextrin nanosponges were prepared by crosslinking. α ,β or γ cyclodextrin with carbonyl diimidazole . In this type of study cyclodextrin based nanosponge formulation were developed as oxygen delivery system. For this purpose, three types of cyclodextrin based nanosponge were suspended in water and were saturated with oxygen and in-vitro characterized. The efficacy was tested on vero cells. This is to check the capacity or ability to release oxygen in presence or in the absence of ultrasound was determined overtime. Cyclodextrin nanosponge or hydrogel combination systems were used for oxygen permeation through silicone membrane [31].
Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infectivity
In one of the research article, it was found that the two types of cellular nanosponges which are derived from plasma membrane from human lung epithelial type II cells or human macrophages. These nanosponges show some protein receptors, both are identified and unidentified, required by SARS-CoV-2 for cellular entry. Then there is the incubation of nanosponges with SARSCoV- 2 takes place which gets neutralized and was unable to infect cells. The nanosponge platform is agonistic to viral mutations. The information on the target of the virus remains the identified host cell; the nanosponge will be able to neutralize the virus [32].
Removal of Neonicotinoid dinotefuran from wastewater
The β-cyclodextrin-based carbonate nansponges are compiled with the superparamagnetic ferrosoferric oxide nanoparticle. In one of the articles it was claimed that the potential removal of Dinotefuran from waste water. The nanosponges – Dinotefuran inclusion were evaluated by Transmission electron microscopy, Energy dispersive spectroscopy, UV-visible spectroscopy, scanning electron - microscopy, Thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray Powder diffraction and Proton nuclear magnetic resonance [33].
Property of having a protective agent from light
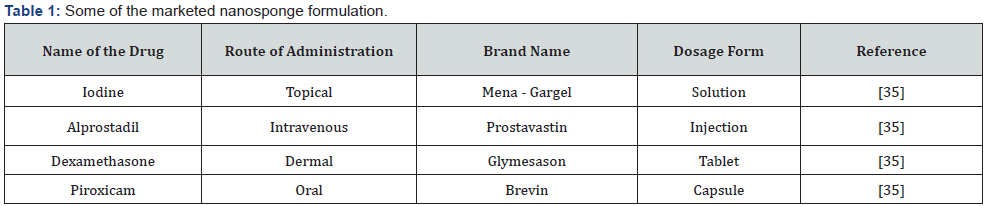
In one of the article, it was encapsulation [34] of Gammaoryzanol showed a good protection from photodegradation. [35] Gamma-oryzanol. This is a ferulic acid ester mixture. Which is an antioxidant are used for stabilizing food and (Table 1) Pharmaceutical raw material [36].
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
Conclusion
In this type of review study, it was found that a nanotechnology type of cyclodextrin-based nanosponge had Pros and cons in the formulation. According to it. It was classified as Plain nanosponge, Modified nanosponge, stimuli-responsive nanosponge, and molecular imprinted nanosponges. Based on it nanosponges technique were used for the synthesis process of nanosponges such as melt- based synthesis, solvent based synthesis, Microwaveassisted synthesis, and ultrasound - assisted synthesis, and useful application of nanosponge in targeted drug delivery system was described in molecular drug targeting, toxin therapy, dermal penetration and as an anticancer therapy.
- Review Article
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Drug Release from Nanosponge
- Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges are Classified into Four Different Stages Depending on Their Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges, Chemical Composition, and Properties
- Techniques Involved in the Synthesis Process for Nanosponges
- Application of Nanosponges
- Conclusion
- References
References
- Rizzi V, Gubitosa J, Signorile R, Fini P, Cecone C, et al. (2021) Cyclodextrin nanosponges as adsorbent material to remove hazardous pollutants from water: The case of ciprofloxacin. Chemical Engineering Journal, 411.
- Ciesielska, Aleksandra Biomedical Application of Cyclodextrin Polymers Cross-Linked via Dianhydrides of Carboxylic Acids. Applied Sciences 10(23): 8463.
- Hoti, Gjylije Effect of the Cross-Linking Density on the Swelling and Rheological Behavior of Ester-Bridged β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Materials 14(3): 478.
- Amer, RehamI (2020) Design and Optimization of Topical Terbinafine Hydrochloride Nanosponges: Application of Full Factorial Design, in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 11(1): 13-19.
- Priyanka, Nagasubba Reddy N, Stella Parusha, Ayyanna, Lavanya, et al. (2019) Fabrication and Characterization of Itraconazole Loaded Nanosponge Gel pp. 1-21.
- Yadav, Geeta Vikram, Hiten P, Panchory (2013) Nanosponges - A Boon to the Targeted Drug Delivery System. Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 3(4): 151-155.
- Simranjot Kaur, Sandeep Kumar (2019) The Nanosponges: An Innovative Drug Delivery System. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research pp. 60-67.
- Rajkondawar, Palesh S, Amit B Patil (2020) Nano-Sponges: A Novel Carrier for Delivery of Chemo-Therapeutic Drugs. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences. pharmascope.org 11(1): 1040-1044.
- Sadhasivam, Janani (2020) Nano Sponges: A Potential Drug Delivery Approach. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 13(7): 3442.
- Balwe, Manish Bandu Nanosponge a Novel Drug Delivery System. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Dosage forms and Technology 12(4): 261-166.
- Ahmed, Rana Z (2013) Nanosponges - a Completely New Nano-Horizon: Pharmaceutical Applications and Recent Advances. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy. 39(9): 1263-1272.
- Singh D, Soni GC, Prajapati SK (2016) Recent advances in nanosponges as drug delivery system: a review. Eur J Pharm Med Res 3: 364-371.
- Caldera F, Tannous M, Cavalli R, Zanetti M, Trotta F (2017) Evolution of Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. Int J Pharm 531(2): 470-479.
- Ma M. Li D (1998) Cyclodextrin Polymer Separation Materials.
- Trotta, Francesco, and Roberta Cavalli (2009) Characterization and Applications of New Hyper-Cross-Linked Cyclodextrins. Composite Interfaces 16(1): 39-48.
- Zhao, Feiping (2015) EDTA-Cross-Linked β-Cyclodextrin: An Environmentally Friendly Bifunctional Adsorbent for Simultaneous Adsorption of Metals and Cationic Dyes. Environmental Science & Technology 49(17): 10570-10580.
- Shende, Pravin (2015) Acute and Repeated Dose Toxicity Studies of Different β-Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponge Formulations. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 104(5): 1856-1863.
- Lembo, David (2013) Encapsulation of Acyclovir in New Carboxylated Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponges Improves the Agent’s Antiviral Efficacy. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 443(1-2): 262-272.
- Rossi Barbara (2015) Toward an Understanding of the Thermosensitive Behaviour of PH-Responsive Hydrogels Based on Cyclodextrins. Soft Matter 11(29): m5862-5871.
- Trotta F, Caldera F, Dianzani C, Argenziano M, Barrera G (2016) Cover picture: Glutathione bioresponsive cyclodextrin nanosponges. Chem Plus Chem 81(5): 433.
- Deshmukh, Kiran (2015) Biomimetic Estimation of Glucose Using Non-Molecular and Molecular Imprinted Polymer Nanosponges. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 494(1): 244-248.
- Satyajit Panda (2015) Int J Pharm Tech Res 8(7): 213-224.
- Tejashri G, Amrita B, Darshana J (2013) Cyclodextrin based nanosponges for pharmaceutical use: A review. Acta pharmaceutica. 63(3): 335-358.
- Singireddy A, Subramanian S (2016) Cyclodextrin nanosponges to enhance the dissolution profile of quercetin by inclusion complex formation. Particulate science and technology.34(3): 341-346.
- Trotta F, Cavalli R, Tumiatti W, Zerbinati O, Roggero C (2008) Inventors; SEA MARCONI TECHNOLOGIES DI W TUMIATTI Sas, assignee. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of cyclodextrin-based nanosponges.
- Chilajwar SV, Pednekar PP, Jadhav KR, Gupta GJ, Kadam VJ (2014) Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: a propitious platform for enhancing drug delivery. Expert opinion on drug delivery 11(1): 111-120.
- Trotta, Francesco (2016 ) Glutathione Bioresponsive Cyclodextrin Nanosponges. ChemPlusChem 81(5): 439-443.
- Hu, Che-Ming J (2013) A Biomimetic Nanosponge That Absorbs Pore-Forming Toxins. Nature Nanotechnology 8(5): 336-340.
- Conte, Claudia (2014) β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges as Multifunctional Ingredient in Water-Containing Semisolid Formulations for Skin Delivery. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 103(12): 3941-3949.
- Mognetti, Barbara (2012) In Vitro Enhancement of Anticancer Activity of Paclitaxel by a Cremophor Free Cyclodextrin-Based Nanosponge Formulation. Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry 74(1-4): 201-210.
- (2016) Ocean Optics Introduces New SERS Nanosponge Substrate for Raman Spectroscopy Applications. AZoNano.Com.
- (2012) Nanosponges - Novel Emerging Drug Delivery System. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research.
- Zhang, Qiangzhe (2020) Cellular Nanosponges Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infectivity. Nano Letters, PubMed Central.
- Salazar, Sebastián (2020) Magnetic β-Cyclodextrin Nanosponges for Potential Application in the Removal of the Neonicotinoid Dinotefuran from Wastewater. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21(11): 4079.
- Ravi, Silpa C (2019) Nano Sponges: A Targeted Drug Delivery System and Its Applications. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences 7(3): 040-047.
- (2020) Orange Book by FDA. Insta PDF.






























