Swallowing Disorders: Dysphagia
*Raniya Naanai
Speech language pathologist At Noor Center for Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation, Casablanca, Africa
Submission: July 31, 2017; Published: August 03, 2017
*Corresponding author: Raniya Naanai, Speech language pathologist At Noor Center for Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation, Casablanca, Morocco, Africa, Email: rania.nanaani@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Raniya N. Swallowing Disorders: Dysphagia. Glob J Oto 2017; 9(3): 555761. DOI: 10.19080/GJO.2017.09.555761
Mini Review
Dysphagia is a disorder of movement that causes either discomfort or difficulty swallowing liquid foods such as solids. Dysphagia is often associated with pathology, but not necessarily. Speech therapist treats dysphagia through rehabilitation.
a) Definition of dysphagia
b) Dysphagia is a symptom that disrupts the swallowing process
c) What is swallowing?
When we ingest food, they are chewed and then directed to the stomach without it implying the airways. It’s swallowing. This mechanism, when disturbed, can initiate the functional and vital prognosis of the person who is affected. This is called dysphagia or swallowing disorders (TD).
a) Dysphagia: a variable symptom
b) Dysphagia can vary from simple discomfort to food passage to food blockade of solids; in this case it is a complete dysphagia.
c) It can also prevent the passage of liquids: it is called aphagia.
d) Dysphagia can be permanent, intermittent, and sometimes even allow easier passage to solid than liquid foods.
Causes of Dysphagia
The causes of dysphagia can be:
i. Mechanical;
ii. Neurological;
iii. Or muscular.
The causes are therefore numerous, we shall cite but a few (Table 1).

Symptoms of dysphagia
Symptoms of dysphagia are many:
a. Inability to swallow saliva;
b. Cough pre, per or post-deglutition;
c. A bolus (a mouthful) comes out through the lips;
d. Printing of food remaining glued into the pharynx;
e. Difficulty in swallowing a bite;
f. Feeling of blockage in the chest behind the sternum;
g. Changes in respiratory rhythm;
h. Dysphagia to solids and liquids
Diagnosis of dysphagia
It is necessary to distinguish between constant dysphagia linked to the swallowing of food (organic damage) and the difficulty of swallowing encountered in an anxious person. The diagnosis must also eliminate cancer of the aero-digestive tract. Here are the successive stages of the diagnosis of so-called esophageal dysphagia, in which the sensation of discomfort is situated in the thoracic cage (Table 2).

Role of the speech therapist in dysphagia
The speech-language pathologist is committed to maintaining autonomy and oral feeding as long as possible. Three criteria guide its action:
a. The recovery prognosis of the patient: can the person recover (cranial trauma, etc.) or should his condition worsen (Alzheimer's dementia, etc.)?
b. Physiopathological observations of the disease provided by functional exploration.
c. The general condition of the patient, as anxiety, fatigue, pulmonary congestion or depression can increase dysphagia.
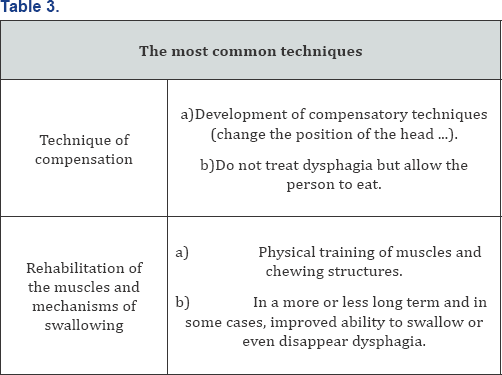
The most common techniques to treat dysphagia in speech therapy are compensation and rehabilitation (Table 3).