Violent Crime in the Context of Entropy Neuron-Glial Networks of the Brain
Rosman SV* and Kurakhina OB
Physician of functional diagnostics of SBIH, Regional psychoneurological clinic, Russia
Head Psychiatric Department of SBIH, Regional psychoneurological clinic, Russia
Submission: July 26, 2017; Published: August 03, 2017
*Corresponding author: Rosman SV, Physician of functional diagnostics of SBIH, Regional psychoneurological clinic, Tver, Russian Federation, Russia, Tel: +7-903-800-11-05; Email: seros2005@mail.ru
How to cite this article: Rosman S, Kurakhina O. Violent Crime in the Context of Entropy Neuron-Glial Networks of the Brain. Glob J Add & Rehab Med. 2017; 2(5): 555599. DOI: 10.19080/GJARM.2017.02.555599
Abstract
The article presents the concept, according to which objective reason violent crime is a psychopathology, which is based on the entropy of a neural network of the brain, a marker which is the variance of the amplitude-frequency characteristics of the alpha rhythm of the EEG (DAFCAR). Defining indexes DAFCAR is possible to predict the potential ability of a person to violent crimes and to develop prophylactic measures to prevent crime.
Keywords: Violent crime; Mental illness; Dispersion of alpha-rhythm; Diagnosis of mental illness
Abbreviations: BPD: Borderline Personality Disorder; CRIM: The Group of Patients who have Committed Violent Crimes; DAFCAR: Dispersion of Amplitude-Frequency Characteristics of the Alpha Rhythm EEG; NGNB: Neuron-Glial Network of the Brain; CDal: Coefficient of Dispersion of Alpha-Rhythm EEG-1(the Quotient of the Modal Values of Power of Alpha Rhythm to his Total Power in the range of 7-13 Hz); CDa2: Coefficient of Dispersion of the Alpha-Rhythm EEG-2(the quotient of the Power of the Alpha Rhythm in the Range of "a Modal Value ± 0.5 Hz” to his Total Power in the Range of 7-13 Hz); HVT: Hyperventilation Test; O Mo f: Value of the Modal Frequencies in Occipital Electrodes; F Mof: Value of the Modal Frequencies in Frontal Electrodes; O Mo f - F Mo f: Value of the Difference of Modal Frequencies Between the Occipital and Frontal Electrodes; IIDA: Integral Index of Dispersion of the Alpha Rhythm EEG (Value of the Kurtosis of the Normal Distribution CDal in the Occipital Electrodes); ADA: Asymmetry Distribution of the Alpha Rhythm EEG (Value of the Asymmetry Distribution CDal in the Occipital Electrodes);IIH: Value of the Index Hypofrontality (Kurtosis of the Normal Distribution CDal in the Frontal Electrodes); AH: Value of the Asymmetry of CDal in the Frontal Electrodes; CV% - the Coefficient of Variation; c.u.: Conditional Unit; Alpha-1/ Alpha - the Share of the Low-Frequency Component of the Alpha Rhythm in the Total Power of the Alpha Rhythm; Alpha-2/ Alpha - the Share of Medium Frequency Component of the Alpha Rhythm in the Total Power of the Alpha Rhythm; Alpha-3/ Alpha - the Share of the High-Frequency Component of the Alpha Rhythm in the Total Power of the Alpha Rhythm; IZ: Index Zoning
Introduction
Modern medical and criminological literature contains many publications linking mental illness and crime, with a particular focus on violent actions, serious injury, murder, terrorism. On 24 March 2015, Germanwings Flight 9525 crashed into the French Alps, killing all 144 passengers on board and six crew members. In the days, that followed, investigators began to suspect that co-pilot Andreas Lubitz had deliberately downed the plane - and when it emerged that Lubitz had a history of depression some questioned whether pilots with similar mental conditions should be allowed to fly. Scientists conducted the study found that a high level of people with abnormal mentality among those convicted of murder (72%) and grievous bodily harm (64,8%) [1]. It was, for example, found that patients with schizophrenia, the crime are a consequence of delusions and hallucinations [2].
According to Planansky and Johnston (1977), violence in schizophrenia patients may be associated with any of the following signs: strong fear and loss of self-control in the presence of non-systemized delusions; irresistible impulses; instructions received from hallucinatory voices; uncontrolled manic excitement; systematized paranoid delusions, including a belief in the necessity to defend themselves from enemies. Taylor (1985), interviewing remand prisoners with psychosis detained in prison, came to the conclusion that the most severe violence in these patients due to psychiatric symptoms [3]. Among the perpetrators of violent crimes, the number called, especially the high level of alcoholism. Noteworthy is the fact that alcoholics markedly less among rapists (four times less than among the offenders who inflicted serious injuries; less than half among murderers). It is clear that rape is mainly a 'youth' crime, and among young people of alcoholics is less than in adults [4].
Among those who have committed a violent crime personality disorders most. Similar to data describing the criminal behavior of persons suffering from residual effects of traumatic brain injury and organic diseases of the Central nervous system. For oligophrenics most typical of the rapes, the rate of which is twice the percentage of murders, thefts, robberies and robberies. A significant part however, the mental retardation are among the bullies. They're distinctive and high levels of alcohol abuse. Due to mental retardation and characteristic appearance they are mostly deprived of the opportunity to satisfy their sexual needs in a normal way and therefore often resort to violence [5].
A comparison of the age of the offenders at the time of committing the crime with the kind of mental anomaly shows that with age, the number of mentally healthy criminals decreases due to, mainly, growth in the number of persons suffering from alcoholism, It is convincing evidence that antisocial lifestyle of constant drunkenness contributes to the emergence and development on this basis of mental anomalies, which, for its part, support this way of life and participate in the determination of criminal behavior. Of course, most alcoholics, getting to places of deprivation of liberty, cease to abuse alcohol, many recover from alcoholism. However, after the liberation, falling into the same or a similar microenvironment, renewing the old way of life, they again begin to drink, swelling the ranks of the offenders with disorders of the psyche. With age significantly increases the number of people suffering from residual effects of traumatic brain injury and vascular diseases mental changes [6].
The most common anomaly among juvenile offenders was personality disorder. If all mental abnormalities among adolescent offenders to take as 100%, the percentage of psychopathy is about 40%. Interestingly, in the age of 18-24 years, the number of psychopaths among criminals compared with age group 14-17 years to be doubled and then gradually reduced. This fact is explained in this article later. In General, we can assume that among offenders aged 18-24 years leading pathology is a personality disorder, and among persons aged 25 years and above with chronic alcoholism [7]. However, Taylor and Gunn (1984) when viewed 1241 defendant in custody in a prison, found a significantly higher prevalence of schizophrenia among those who were subsequently convicted of murder and arson, than one would assume based on the prevalence of this disease in the General population [8].
Is there a relationship between all these facts and what can be the true cause of all these deviations of behaviour? Recently in medicine there has been an interesting trend - the occurrence in it representatives of other professions. Would be welcome this process (at the intersection of science is born the most interesting), if not for the commitment of these professionals, without formal biological education, with aplomb to teach doctors. Somehow I have not seen the outstanding neuroscientists involved in Fermat's great theorem and not because the mathematics is more complicated neurophysiology, and because medicine is more difficult to argue - it is very much unknown.
And so the crime problem - to understand the multiple psychological and social turns in it, created a speculative scheme that relies exclusively on mind games, it is not taking into consideration that, ultimately, everything - drugs, alcohol, and promiscuous life, and psychological overload, characteristic of the criminal environment - all this leads to the destruction of the brain, and its neuron-glial network. And so many answers to questions of crime should be sought in the study of the peculiarities of the brain of criminals.
In this article, we proceed from the fact that the basis of human behaviour is a process of interaction between afferent information and the information part of man, whereby is produced a behavioral response in the form of efferent response [9]. The intermediary in this process is the NGNB. If NGNB is in the normal functional state, the process of reunification proceeds correctly if there are functional abnormalities, errors occur (information distortion). These simple arguments and are the basis of attempts to find violations to the NGNB, that underlie deviant behavior [10].
The purpose of the study
To prove that the basis of deviant human behavior and violent crime, in particular, are the processes of destruction MSGM, the degree of which can be verified by measuring indices of DAFCAR.
Materials and Methods

In the group CRIM was studied EEG 145 men at the age of 36.2 years (30.2 - 42.2, CV%=31%), subjected to forensic psychiatric examination, which was charged with violent crimes - murder and causing grievous bodily harm. A control 44 recruit in the Armed Forces at the age of 20.8(19.4 - 22.2 CV%=22%) years recognized by Commission of experts mentally healthy. EEG was carried out according to standard methods with the imposition of the electrodes according to the international scheme "10-20%" with the ipsilateral ear electrodes, as well as the identification of indicators, DAFCAR and HVT according to SV Rosman [11-18]. Data were processed by means of mathematical Statistica 10.0 software. It is established that by results is judicial-psychiatric examination in the group CRIM diagnosis recorded the following diseases (Table 1).
Thus, it is clear that predominant in the study of this group was the presence of severe mental illness (76%).
Further definition of indicators DAFCAR and type of reaction on HVT revealed the following. Visual assessment of maps reveals the following features (Figure 1):
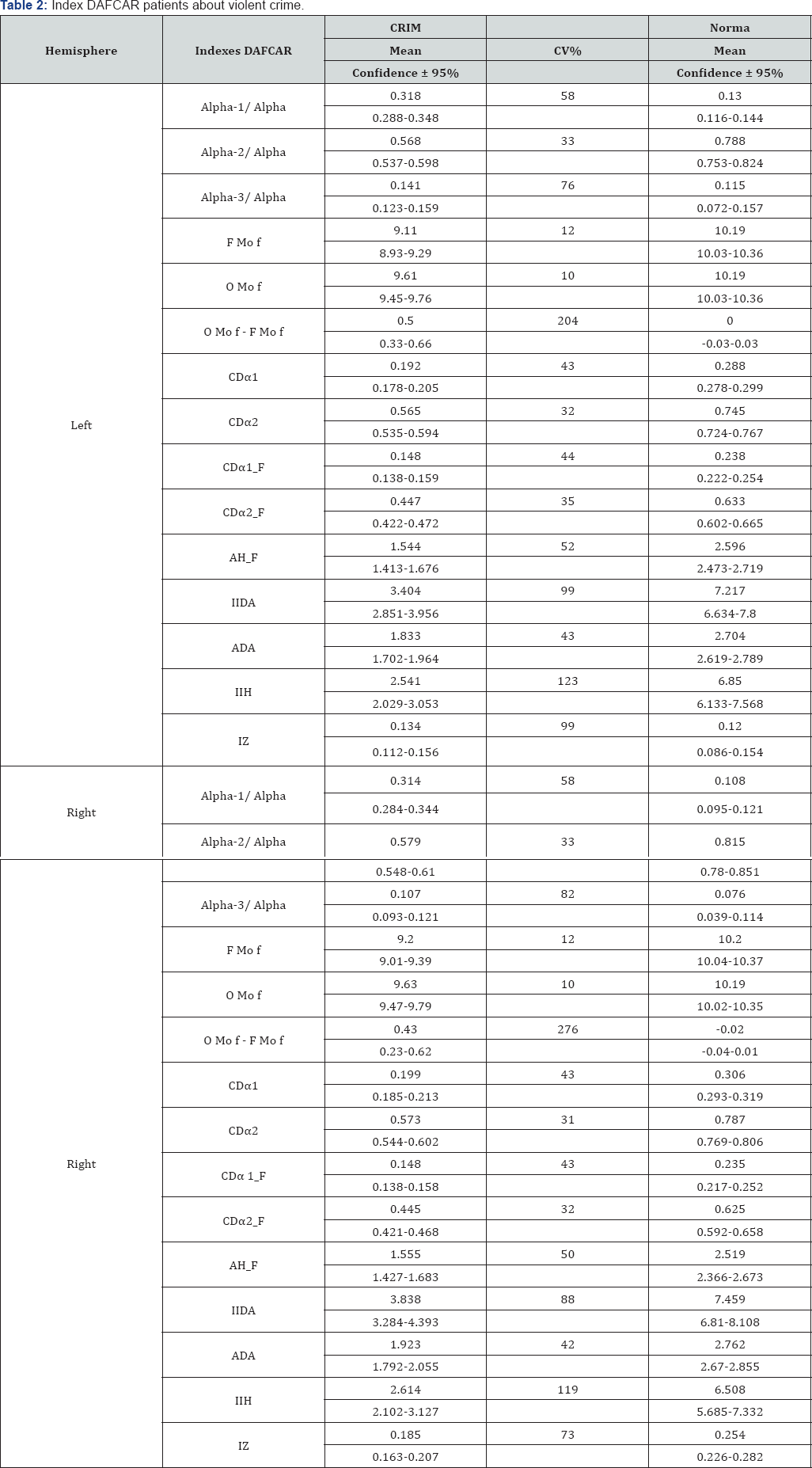
a. The overall modal frequency (OMo f) is at the lower limit of normal (about 9.75 Hz) with mind-Rennes increase dispersion of the alpha rhythm.
b. There is a gradual increase in the representation of low-frequency component of the alpha rhythm in the frontal electrodes with the displacement of the modal frequency (F Mo f) to 0.5 Hz.
c. Dispersion changes in the frontal electrodes are moderate.
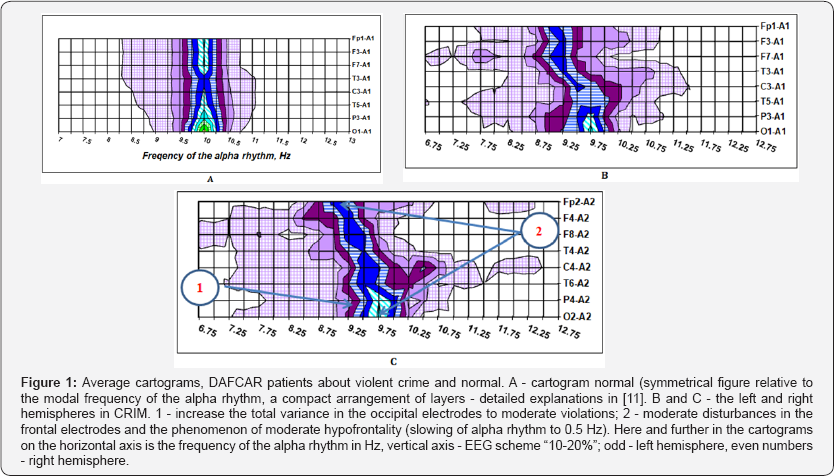
Analysis of indexes DAFCAR fully confirmed by the data of visual evaluation of cartograms (Figures 2 & 3):
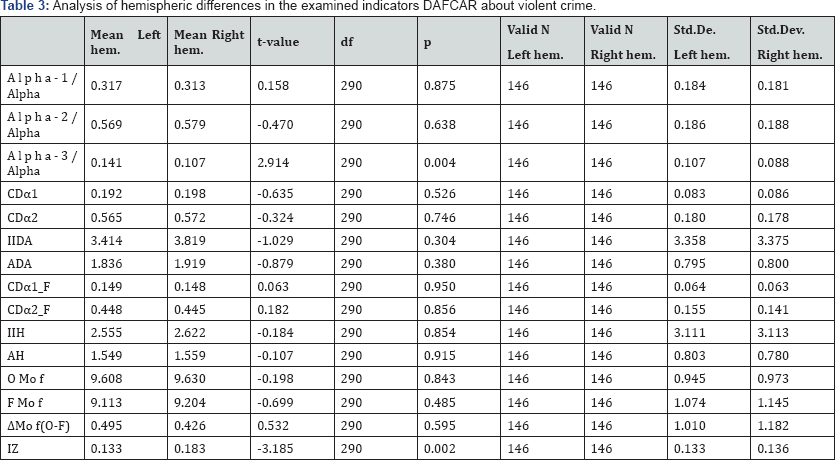
- Differences in the rate of DAFCAR hemispheres statistically significant (Table 2). There are some minor fluctuations in the high frequency representation of the alpha rhythm and zonality index in the normal range (higher in the right hemisphere).
- There is a moderate difference from that of normal (Table 3)
- The overall modal frequency (OMo f) is at the lower limit of normal (9.45-9.76 Hz) with a moderate increase of dispersion of the alpha rhythm compared to the norm.
- There is a gradual increase in the representation of low-frequency component of the alpha rhythm in the frontal electrodes with the displacement of the modal frequency (F Mo f) to 0.5 Hz.
- Dispersion changes in the frontal electrodes are moderate (mild-moderate degree of hypofrontality).
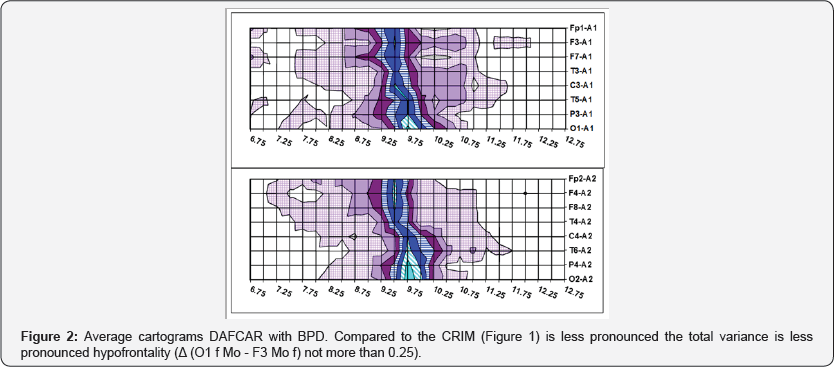
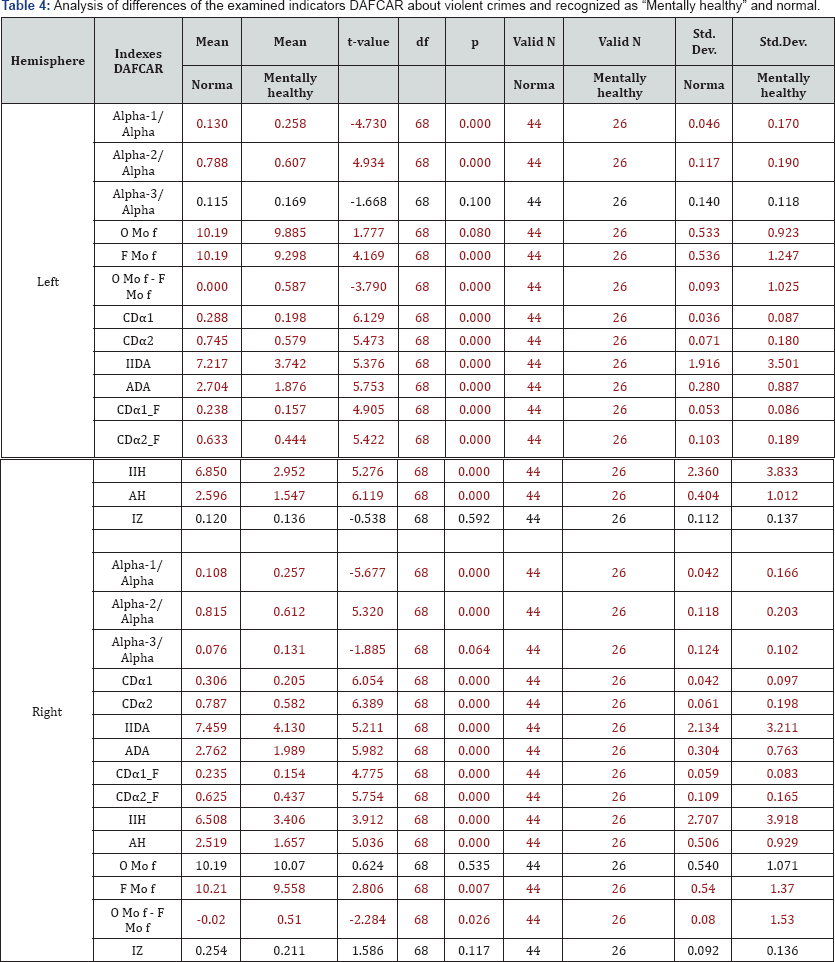
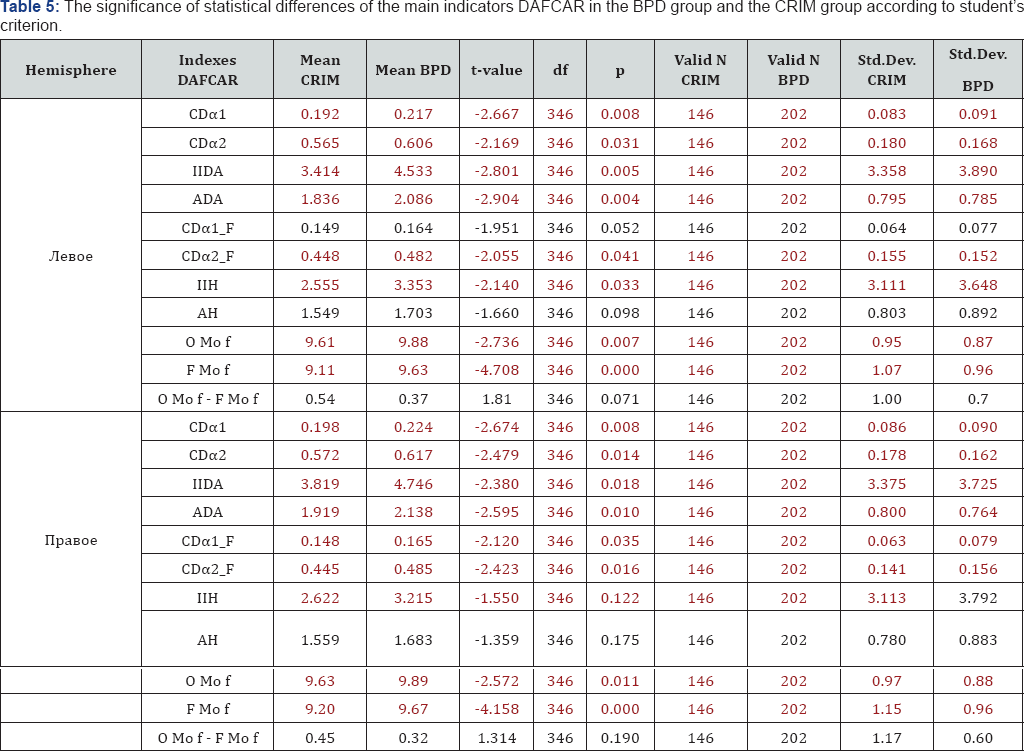
Of particular interest is a clinical and neurophysiological mapping indicators DAFCAR and HVT and patients recognized experts "Mentally healthy". Of the 26 cases Table 1, normal indices DAFCAR had only 7; their average statistically significantly differed from values in the control Table 4. Of these, 5 patients had endogenous type HVT, i.e. subcompensation violations in NGNB. A total of 145 surveyed about violent crimes, only 2 patients could be considered healthy on clinical and neurophysiological indices (1.4%). Parameters DAFCAR in the CRIM group close to those observed in BPD [14]. However, there are observed time differences (Figure 2, Table 5). Quite revealing are the results of HVT. In the CRIM group resulted in significant (more than 2-fold) relative increase in the number of endogenous response types (Figure 3).
Note: Values highlighted in red font are statistically significant differences in the compared groups.
Note. Values highlighted in red font are statistically significant differences in the compared groups.
Discussion of the Results
The study of the place, which is a person prone to violent crime outside the context of the adopted systematization of mental diseases according to nosological forms, and in accordance with the degree of entropy NGS GM leads us to very interesting conclusions. "We all come from childhood" - is banal at its core, the observation has deep physiological roots. Indeed, how he spent his childhood people, the conditions in which he was raised, leaves a deep mark on all his behaviour for the rest of his life. Unique research LB Ivanov (2016) [6] show that accelerated entropic processes in NGNB in the form of increase of the variance of the alpha rhythm and, especially, hypofrontality can be a source of psychopathology in adulthood. In children the phenomenon of dispersion can be a symptom of neurophysiological immaturity (NPI) and a variant of normal development, but to a certain degree and a certain age.
By the end of puberty signs NPI must be reduced, and after the age of majority to disappear altogether. Children of variance violations NGNB can cause behavioral disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and somatoform disorders. In adults surviving childhood changes appear DAFCAR DPD and severe psychopathology. Thus, even in childhood, according to EEG research, it is possible to predict the likelihood of the child deviant, and potentially criminal, behaviour. Despite the fact that some signs point to a significant shift in the "axis of dementia" in the field of pathology, some other signs point to boundary nature of the changes - with an increase in the total dispersion changes signs of hypofrontality remain largely unchanged. Anyway, we obviously are dealing with obvious signs of increase DAFCAR. Especially revealing are the results of HVT: number of endogenous and exogenous reactions is doubled, indicating a significant pathological background in NGNB.
These data explain repeatedly described the subject of the phenomena which are usually related either to the attempts to evade responsibility, or to the effects of alcoholic intoxication. We are talking about when they describe the feeling that everything is not with them but with someone else that they couldn't commit, etc. To some extent we are talking about depersonalization. The HVT results show that this phenomenon has an objective confirmation. The results of comparative studies of HVT (Figure 3) show that the CRIM group significantly increased the number of individuals with endogenous reactions, including in the group of "Mentally healthy", which in 7 cases the index DAFCAR was normal, but of these 5 patients had HVT endogenous reaction type. This indicates subcompensated nature of entropy NGNB.
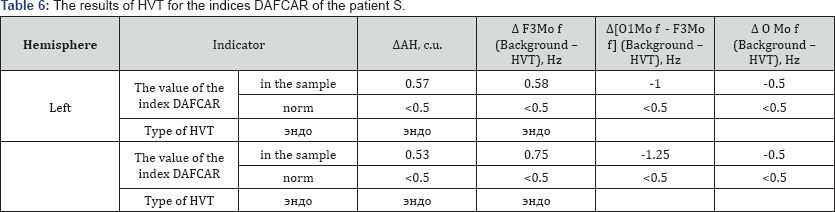
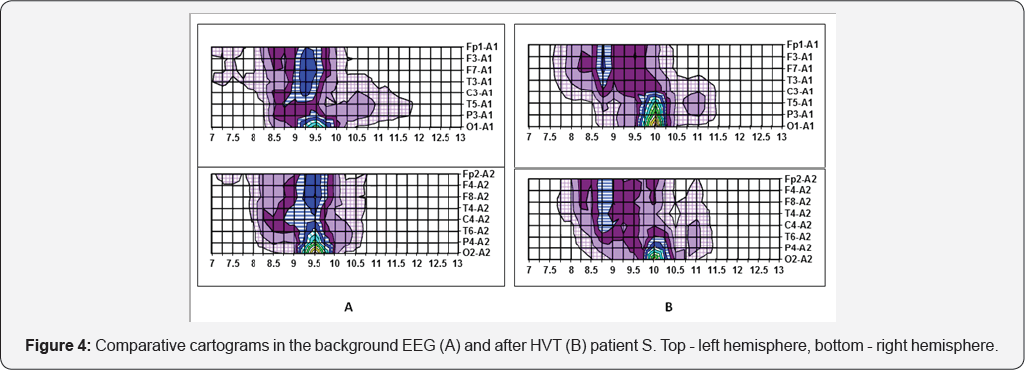
Depersonalization is a frequent accompanying symptom of schizophrenia. Schizophrenia, as has been shown in studies, DAFCAR, accompanied by the dispersion characteristics of functional hypofrontality [15]. This reaction in its neurophysiological indicators of DAFCAR reminiscent of the changes characteristic of schizophrenia. It is possible that stress or intoxication such patients experience a near schizophrenic attack. Here is a clinical example patient S., who several years ago killed his mother with a knife. A panel of psychiatrists he was found in need of involuntary psychiatric Le increase, but the diagnosis of schizophrenia was not present. After 4 years he was discharged to outpatient treatment and does not manifest itself, the treatment is accurately received. This year, after a long conflict with a neighbor, he has committed his murder with a few strokes of the knife. Below are the dispersion diagrams of the patient C. in the background EEG after HVT.
Obvious signs of sharply increasing hypofrontality after HVTof significant displacement modal frequency of the alpha rhythm in the frontal electrodes in the low frequency area toward the occipital electrodes and the increase of the dispersion changes. Thus, we can simulate schizophreniform changes to the NGNB under the action of a stressful situation. It is quite natural to assume that the patient has the symptoms of depersonalization that can cause totally inadequate actions and even delusional personality disorder, as in schizophrenia (Figure 4)
When clinical data do not coincide with neurophysiological, from psychiatrists to hear the following "argument": "But the patient is clinically nothing. Somehow overlooked the fact the hardest of deviant behaviour violent crime. Somehow, he always stays out of the discussion. The large discrepancy is easily explained - many psychiatrists are convinced that EEG studies are non - specific, and pay attention to them is not really worth it, but it is a profound error. In medicine there are a number of non-specific research, without which the correct diagnosis is very problematic - for example, body temperature in the General examination and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in laboratory diagnosis. Of course, the method must pass the tests in order to develop common criteria and standardization. Conducted studies amply confirm the fact that the nonspecific nature of the indicators DAFCAR are informative enough to identify the entropy of NGNB underlying deviant behaviour

If we try to determine the place that took patients from the group on the CRIM " axis of dement " [11], they are located while in the area of psychopathology, but close enough to the BPD (Figure 5), and this is related to numerous expert difficulties can be overcome, given the data DAFCAR. It is clear that EEG data can serve as evidence of guilt in the pre-jet or his propensity for violence. Rather, they are preventive in nature, directing the attention of the psychiatrist to the possibility of inappropriate behaviour in this patient the need for treatment and preventive measures. Especially big roll study DAFCAR may have in the work of expert committees to identify the decreed contingent - enlisting in the Armed Forces and law enforcement agencies, access to weapons possession and particularly dangerous and complex forms of activity (transport dispatchers, pilots, public transport drivers) [9]. These studies, after appropriate analysis, can serve as a criterion of recovery of the mentally ill, especially after the forced treatment regarding violent crimes and to develop appropriate recommendations for their surveillance for outpatient treatment.
Conclusion
a) The overwhelming majority of people(98.6%) committed a violent crime represented-based study had signs of increase of entropy NGNB, manifested by decrease in indexes DAFCAR
b) Conducting EEG with a calculation of the indices DAFCAR and HVT according to SV Rosman allows on early stages to identify violations and monitor during treatment and preventive measures.
c) We present a methodology for the study DAFCAR, after proper testing and standardization can become a veryvaluable expert verification work psychiatric committees for the purpose of identification when applying for service in the Armed Forces and law enforcement, admission to possession of a weapon and dangerous and complex forms of activity (transport dispatchers, pilots, public transport drivers).
References
- Rowe M, Baranoski M (2001) Mental illness, criminality, and citizenship. J Am Ac Psychiatry Law 28(36): 262-264.
- Liebert JA (1985) Contributions of psychiatric consultation in the investigation of seial murder. Int J Offend Their Comp Crimin 29: 187200.
- Hersen M, Ammerman RT, Sisson LA (1993) Handbook of aggressive and destructive behavior in psychiatric patients/ Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA.
- Mokeev IB (2008) Mental disorders, alcohol and drug abuse as etiological factors for criminal aggression. Russian journal of psychiatry N l. C. 5 (In Russia).
- Ivanov NG (1998) Abnormal offender. Problems of criminal responsibility. UNITI, (In Russia), Moscow.
- Gelder MG, Geddes JR, Andreasen NC None, Lopez-Ibor JJ (2009) None New Oxford textbook of psychiatry, Oxford, UK, pp.l09-ll5.
- (2013) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, (5th edn) (dSM-5). Arlington, VA, USA.
- Cooper B (2001) Nature, nurture and mental disorder: old concepts in the new millennium. Brit J Psychiatry 178(40): 91-102.
- Graham Loren R (1987) Science, Philosophy, and Human Behavior in the Soviet Union, Columbia University Press, USA.
- Sanislow Charles A (20l6) Updating the Research Domain Criteria. World Psychiatry 15(3): 222-223.
- Rosman S (2017) The Theoretical Foundations of Dispersion of Amplitude-Frequency Characteristics of the Alpha Rhythm of the EEG. Glob J Add & Rehab Med 2(3): 555587.
- Rosman S (20l7) The Use of Analysis of Variance of the Alpha Rhythm of the EEG in the Study of the Pathogenesis of Alcoholism and the Causes of Alcoholic Deliria. Glob J Add & Rehab Med 2(1): 555580.
- Rosman SV (2013) Diagnostic capabilities of dispersion mapping the alpha rhythm of the electroencephalogram. Mental health 6: 64-69. (In Russia).
- Rosman SV (2017) Borderline Personality Disorder in the Context of Entropy Neuron-Glial Networks of the Brain. Glob J Add & Rehab Med 2(4): 555595.
- Rosman SV (2013) Opportunities of the dispersive mapping of the alpha rhythm of electroencephalogram in diagnostics of schizophrenia. Psychiatry 2: 32-37 (In Russia).
- Rosman SV, Shpak LV (2013) New approaches to the assessment of polymorphism of the alpha rhythm of the electroencephalogram with mental illness. Mental health (2): 39-44. (In Russia).
- Maximova NE, Rosman SV, Shpak LV, Zabodaev SV (2016) Possibilities of use of dispersion of an alpha rhythm for screening verification of mental diseases. Mental health 1: 16-25 (In Russia).
- Ivanov LB (2016) Psyco-phisiological interpretation of the functional state of the brain using EEG. Bullet clin Neurophysiology (1): 5-26.






























