The Effectiveness of Parent Training with Adlerian Approach on the Coping Methods among Mothers of their Children with Conduct Disorder
Somaieh Salehi*
Department of Psychology, Shahid Beheshti University, Iran
Submission: January 16, 2018; Published: April 02, 2018
*Corresponding author: Somaieh Salehi, Department of Psychology, Family Institute, Professional Family and Child Clinic, Shahid Beheshti University, Tehran, Iran, Email: somaieh19salehi@gmail.com
How to cite this article: Somaieh Salehi. The Effectiveness of Parent Training with Adlerian Approach on the Coping Methods among Mothers of their Children with Conduct Disorder. Glob J Arch & Anthropol. 2018; 3(3): 555611. DOI: 10.19080/GJAA.2018.03.555611
Abstract
Objectives: The present research aimed to examine the effectiveness of parent training with Adlerian approach on the coping methods among mothers of children with Conduct Disorder.
Methods: The used research design in this research was pre-test-post-test and with control group and quasi- experimental design. Hence 30 mothers from clients to psychiatry section (behavioural disorders) of Baghiata Allah Azam Hospital in Tehran were selected on the bases of convenience sampling method in 2016 and were arranged in experimental and control group. Experimental group received parent training with Adlerian approach and control group was not received any training. In this research two instruments of Child Behaviour Checklist (CBCL) and Coping Inventory Stressful Situations were used for diagnosis and intensity of conduct disorder and considering of coping methods and for analysis of data the t-test was applied.
Results: The results of data analysis have indicated the effectiveness of parent training with Adlerian approach on the coping methods of mothers of children with Conduct Disorder. Research hypotheses regarding the changing of coping methods and decreasing of conduct disorder symptoms were confirmed with 95 percent confidence interval.
Conclusion: Consequently the findings of this research have indicated the effectiveness of parents training with Adlerian approach on the coping methods of mothers of children with conduct disorder.
Keywords: Conduct disorder; Adlerian approach; Parent training; Coping methods
Abbreviations: ADHD: Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder; ODD: Oppositional Defiant Disorder; CD: Conduct Disorder; PMT: Parent Management Training
Introduction
Today, regarding this point that parents face a lot of difficult challenges for training their children, if their children is stricken to behavioural disorder, they may feel apparently disappointment and prostration. However, children play an important role in making their problem and they are responsible for the majority of the parents-child problems, but it is the parents that are in the best situation of helping that child and they can change the importance of the relationship. In fact, the researches done show that those groups of child oriented interventions that the parent played an active role in them have a better efficiency compared to those that put their focus only on the child. So, in the family that there is conduct disorder, the active cooperation of the parents in the situation improvement is necessary [1].
Behavioural Disorders
The behavioural disorder expression came to the psychology emotional and motion ability and physical growth. literature culture about 85 years ago. From then on, teachers,psychologist, nurses and others that were interested in children's emotional and behavioural problems used this term for expressing their intent, but there isn't any globally accepted definition for it yet. Rhodes and Paul (1978) believe that this expression lacks a clarity because of the different ideas and views presented by various specialist in social sciences disciplines. Some definition of behavioral disorder includes but not limited to:
a. A child has behavioural disorder when it has a lack in his behaviours and performances compared to the children of the same age.
b. A child that has one of the below characteristics at the cause of physical or environmental effects:
c. Disability in learning considering intelligence quotient, The behavioural disorder expression came to the psychology emotional and motion ability and physical growth. literature culture about 85 years ago. From then on, teachers,
d. Disability in making and keeping the appropriate social
relationships
e. Disability in response to daily conditions of life
f. Various radical behaviours that results in hyperactivity disorder or immediate response and depressed behaviours (Haring, 1963).
Different Types of Behavioural Disorders
In the fourteenth edition of diagnostic & statistical manual of psychiatric disorder (American Psychiatric Association, 1994), three types of behavioural disorder have explained that include:
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a condition that becomes apparent in some children in the preschool and early school years. It is hard for these children to control their behaviour and/or pay attention. The principal characteristics of ADHD are inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Symptoms of ADHD will appear over the course of many months, often with the symptoms of impulsiveness and hyperactivity preceding those of inattention, which may not emerge for a year or more. Different symptoms may appear in different settings, depending on the demands the situation may pose for the child's self-control.
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)
ODD is a psychiatric disorder that is characterized by two different sets of problems. These are aggressiveness and a tendency to purposefully bother and irritate others. It is often the reason that people seek treatment. When ODD is present with ADHD, depression, tourette's, anxiety disorders, or other neuropsychiatric disorders, it makes life with that child far more difficult. For Example, ADHD plus ODD is much worse than ADHD alone, often enough to make people seek treatment.
Conduct disorder (CD)
Conduct disorder (CD) is one of the most common psychiatric disorders in childhood and adolescence. It is characterized by a variety of chronic antisocial behaviours, major age-appropriate social norms, or both. Aggressive behaviour, lying, stealing, fire- setting, and running away from home and school are the most frequent manifestations of CD and are often accompanied by hyperactivity impulsive, behaviour, explosiveness, cognitive and learning problems, and poor social skills.
Coping
Fulfilling weak role by incompetent parents affects the children that have the Conduct Disorders a lot. Parents may show different responses in the behaviour problem of their children. It can be consider as coping. Coping means the attempts done for the control and management of situations that seems dangerous and stressful. Three coping approaches discussed repeatedly in research literature are: task coping, emotion coping and avoidance coping.
Task coping
This kind of coping can be internal or external. The goal of external task coping is changing the others' situation or behaviours, but the internal coping includes the attempts done for the re-examination of attitude, needs, skill inception and new responses.
Emotion coping
Emotion coping is an approach that is more expanding than social support scale in coping approach indicator. Emotion coping shows a form of reaction to stressful events that may need reliance on the others [2].
Avoidance coping
This kind of coping is denoted by the lack of the attempts for situation change (situation avoidance, denial of situation existence).
Parents may experience different stresses such as personal stress, matrimony relationship stress and child rearing stress in their own life. These stresses can lead to unsuccessful upbringing of the child and consequently child conduct problems. The parents that their stress is average or low can use different coping methods. In such cases, it is necessary to do some actions for prevention, intervention and assistance of the parents and children. Parents training program is one of such actions. Parent training means therapeutic interventions that in it one or both of the parents are trained to interact with the children in a different manner.
In this program the emphasis of most of the elementary guidance for parents is on the reinforcement of conduct and relational skills in order to learn them the way of making the relationship and interact with their children. These principles, diversifies individual psychology from the other theories.
Adlerian Approach
Individual psychology was introduced by Alfred Adler. This theory was psychological, cognitive, and social and includes believes and understandings of a person. Adler is one of the psychologists that was interested in democracy in home, school and work environment. Clinical researches on the families that their child is stricken by a chronic disease show the need of the assessment of coping reactions of parents. This helps the researchers to determine the amount of the parent consistency in order to receive necessary support and training if professional assistance and intervention is needed for increasing the effects of the coping methods. Besides the children, in this matter, it is necessary to consider the parents that have children with a problem. Since the parents play an important role in children improvement and they need to pay attention to coping methods with children conducts, so it’s necessary to receive useful information and training.
Ample researches have been done about the effect and use of Adlerian approach on the change of children upbringing methods of parents. Since the parents choose different coping methods in relationship to themselves and their children and because of the shortage of researches done about the mothers with conduct disorder children especially in the case of training in Iran, this research that focused on Adlerian approach is to hold some training programs for mentioned mothers on the basis of Adlerian approach.
Behavioral Parent Training Programs
This group of programs teaches parents of a difficult child how to discipline the child more effectively and control overt conduct disorders. The programs are highly structured and trainers use programmed instructional aids and manuals with special topics and exercises with homework assignments each week. Typically a course includes 8 to 14 weekly sessions lasting about 1 to 2 hours. Skills typically taught include behavioural shaping principles of positive reinforcement, attending to wanted behaviors and ignoring unwanted behaviours. Approximately 50% of all children diagnosed with conduct disorders develop delinquency in adolescence and the others often show other social and developmental problems (Kazdin, 1987).
Of the psychological therapies, parent management training (PMT) is the method demonstrated to have the most impact on the child's coercive pattern of behaviour. PMT refers to procedures in which parents have been trained to alter their child's behaviour in the home. PMT is based on research demonstrating that conduct problems inadvertently are developed and sustained by maladaptive parent-child interactions. While this conflictual interaction often is triggered by the irritable temperament in the child, a major component of this pattern is ineffective parenting. This includes the parent directly paying attention to disruptive and deviant behaviours but using unclear vague commands and directions and inconsistently applied harsh punishment. A pattern of failing to pay attention to appropriate behaviours, when they occur, is also present.
PMT alters the pattern of ineffective parenting by encouraging the parent to practice prosocial behaviour (positive, specific feedback for desirable behaviour), employ the use of natural and logical consequences, and use effective, brief, non-aversive punishments on a limited basis when specific encouragement and consequences are not applicable.
PMT educators and therapists teach the child’s parents to use specific procedures at home to alter interactions with their child. Parents are trained to carefully identify and observe behaviours and to reinforce desired behaviours. Training sessions provide opportunities to see how procedures work and to practice and refine their use of techniques [3].
Adlerian Parenting Program
These programs are based on clinical psychology principles of improving the whole person. Dinkmeyer and McKay's (1976) Systematic Training for Effective Parenting (STEP) is based on the theoretical teachings of Alfred Adler. This program involves local groups of parents in 8 to 12 weekly two-hour sessions covering parenting topics such as understanding the child’s behaviour and emotions, using encouragement, listening and communicating more effectively, disciplining by using natural and logical consequences rather than punishment, establishing family meetings, and developing confidence as a parent. The goal of this program is to improve the child's self-concept and dignity.
The Adler School of Professional Psychology has long been a proponent of respectful parenting and the skilled delivery of effective discipline in our changing world. Building on the solid foundation of effective research-supported parenting methods, they are incorporating a range of knowledge and skills that make their CARE program a truly holistic approach to parent education - as reparative and as preparation.
The topics they cover in a hands-on manner are geared specifically to those they teach. A respectful disciplinary approach informs all their offerings which focus on three dynamic aspects of child rearing: child development (and the stresses that occur when this is disrupted by separation from the children); care-giving from outside the family (including day care and school involvement); child enrichment (playtime and spirituality).
Between eight and twelve hours of instruction is provided depending on the combination. The modules will be provided in six, two-hour sessions, although the format is flexible. Instructors are graduate-level clinicians. They receive hands-on instruction in the art of teaching parents the application of theory.
Following are the major areas addressed and some of the topics covered in each session.
a. Effective Respectful Discipline I: Parenting as a process; Understanding yourself and your children; Encouragement; Self-esteem; Communication.
b. Child Development: Stages of growth; Intellectual development; Social development.
c. Effects of Separation on Children: Divorce issues; Domestic violence and its effects; Incarceration and returning to the family.
d. Interacting with Alternate Care-givers: Placement and visitation with Foster Parents; Co-parenting as a possibility.
e. Effective Respectful Discipline II: Understanding and redirecting misbehaviour; Types of families; Natural and logical consequences.
f. Locating and Monitoring Child Care: How to find the right centre for your children; Interviewing and interacting with the day care centre staff; Determining eligibility for financial assistance; Transportation to/from day care centre.
g. Interacting with the School System: Remembering your school days; Doing your share, allowing the school to do theirs; Getting academic help for your children.
I How to cite this article: Somaieh Salehi. The Effectiveness of Parent Training with Adlerian Approach on the Coping Methods among Mothers of their Children with Conduct Disorder. Glob J Arch & Anthropol. 2018; 3(3): 555611. DOI: 10.19080/GJAA.2018.03.555611.
h. Effective Respectful Discipline III: Redirecting with natural and logical consequences; Family meetings.
i. Planning Age-appropriate Playtime: Learning what kids can do (review of developmental stages); No need to buy it! (Making fun toys from household items); When to help and when to leave 'em alone (Age-appropriate interaction with children).
j. Spiritual Enrichment of Child-Parent Relations: Religion and discipline (The importance of not confusing them); Religion and spirituality (Telling them apart); Understanding the stages of spiritual development (When to encourage and when to back-off).
Research Methods
Purposes
The main purpose of this research is to determine the amount of the effectiveness of parents training with the Adlerian approach on copying methods of mothers of conduct disorder children. Regarding the mentioned debates, the main question of this research is to find an answer to this question that if the parents training with the Adlerian approach affect coping methods of the mothers of conduct disorder children?
Main hypothesis
Parents training with the Adlerian approach affect coping methods of the mothers of conduct disorder children.
By product hypothesis
a) Parents training with the Adlerian approach affect the decrease of avoidance coping method of the mothers of the conduct disorder children.
b) Parents training with the Adlerian approach affect the decrease of emotional coping method of the mothers of conduct disorder children.
c) Parents training with the Adlerian approach affect the increase of coping method of the mothers of conduct disorder children.
d) Parents training with the Adlerian approach affect decrease of the symptoms of the conduct disorder children.
Research Design
The used research design in this research was pre-test and post-test quasi- experimental design with control group.
Subjects
Statistical society of this research were the mothers having son children from 7 to 10 years old with conduct disorder that referred to psychiatry section(behavioural disorder section) of Baghiatallah Azam Hospital in 2016. In sampling this research used from available sampling method. The group of experimental and controlling were selected from psychiatry section (behavioural disorder section) of Bghiatallah Azam Hospital at convenience sampling method. The sampling group - that cooperated voluntarily- were 30 persons from which the 15 persons replaced in experimental group and other 15 persons in controlling group at random basis (15 mothers had the son children having conduct disorder from 7 to 10 years whit emotional and avoidance coping method as experimental group and 15 mothers had the son children having conduct disorder from 7 to 10 years whit emotional and avoidance coping method as controlling group).
Research tools
In this research for obtaining the information in addition to using from library sources for theoretical study and adjusting the research literature the Child Behaviour Checklist (CBCL) and Coping Inventory for Stressful situations were used.
a. Child Behaviour Checklist (CBCL) in this study to see the changes about aggression among children with Conduct Disorder. The psychiatrist of the centre conducted a Structured Clinical Interview with both children and their parents to select children with Conduct Disorder and childhood-onset type based on DSM-IV-TR criteria. The psychiatrist checked the following criteria for the participants of the study:
i. Moderate severity of CD
ii. Childhood-onset type of CD
iii. The age between 8 and 10 years old
iv. Normal intelligence
v. No Comorbidity with This questionnaire was normed by Minaii at Tehran in 2005 [4].
b. Coping Inventory for Stressful Situations This inventory was translated and normed by Mr. Akbarzadeh at Tehran in 1992.
Research Procedure
First, in this research the questionnaire of Achenbach (CBCL form) and Coping Inventory for Stressful Situations were distributed between mothers that reoffered to psychiatry section (behavioural disorder section) of Bghiatallah Azam Hospital for diagnosing of coping method of mothers and selection the mothers that have son children with conduct disorder (7 to 10 years old). This work lasted for 1 month. Considering in this section it was necessary that the children of mothers having slight conduct disorder were selected. The result of Achenbach questionnaire (CBCL) shows that the children of this mother have the least score for conduct disorder. Hence pre-test was done before the first session.
Between this person 15 mothers had the son children having conduct disorder from 7 to 10 years whit emotional and avoidance coping method as experimental group and 15 mothers had the son children having conduct disorder from 7 to 10 years whit emotional and avoidance coping method as >controlling group. Experimental group was trained weekly vide 45-60 minute sessions with Adlerian approach and controlling group was never received any variable [5,6].
This training was designed with regard to Adlerian approach concepts and parent training with Adlerian method briefly with emphasizing to cognition of life style, changing of their life style, reviewing to pampering parent and coercive parent life style, cognition and changing of mothers believes, creation of insight and conscious regarding to life stresses and expressing of the relation among stresses with the behavioural parent problems, awareness of parents with regard to the family environment and expressing the relation between them and effectiveness of their and children behaviour, familiarizing of mothers with misbehaviour reasons of child and their performance, explaining of appropriate encouragement and training of proper methods of obeying children from mother's instructions, training of social behaviour skills to child, training of proper expressing violent to children and utilization training from logical and natural outcomes. After treatment course in 10th session which was held with the gap of 2 weeks after 9 sessions, the both questionnaires were performed again.
Results
For data analyzing we have used from descriptive statistic and also from inferential statistic in proportion which it is in connection to descriptive statistic from frequency, mean and standard deviation and also in connection to inferential statistic from parametric t-test calculation (SPSS 18). The aim of t-test investigation is comparison of means in two groups such as experimental and control provided that the observed differences is confirmed in the view of statistical index, refusal zero assumption and opposite assumption are confirmed.
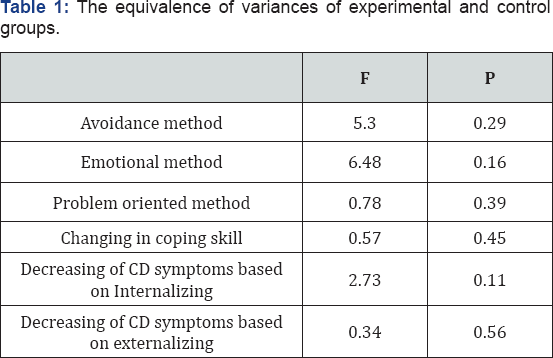
In SPSS plan a test for equivalence of two group variances is used. With regard to results of table 1 significance of avoidance, emotional and task coping methods, the changing of coping methods and also reduction of conduct disorder symptoms (in view of DSM criteria and extroversion) is greater than 0.05 which shows that the variances of two groups are equal (Table 1). Significance result interpretation of means differences regarding the scores of CISS and ASEBA questionnaire in experimental and control group shows that aggregate scores of CISS in the mothers that have been trained under Adlerian approach in comparison to control group enjoys from significance difference P<0.05, also in ASEBA questionnaire (CBCL form) the assumption of this research was confirmed in P<0.05.
Discussion
In general, attention is paid to the theoretical aspects of the research in relation to the wide range of Adlerian approaches to the family and the relationship between the child abuse and the family environment and the beliefs of the experts that the biological reality of parenthood by themselves conferred on them the effective skills of raising a child. And the need for parenting has shown that skills that are taught to parents in a child-rearing education program helps them reduce violence and disobedience in their children, which is the whole of the family’s tissue.
Also, according to the theoretical issues of the research, the effect of parental education programs on their parenting skills and the positive effects on changing behaviours and their compatibility with their children, the effect of parent education on decreasing aggression of children, the stability of these changes, the emphasis of parent education with Adleri approach to avoiding punishment, the use of encouragement, attention to the logical and natural consequences, lifestyle and the application of these concepts in educational and research sessions on parenting coping strategies in relation to their child’s behavioural problems and the effectiveness of Parenting training emphasizes the results of this advocacy therapy.
Research Limitation
Limitation under researcher selection
a) The limitation of research accomplishment in Baghiatallah Azam hospital.
b) The limitation of research accomplishment time which only bound to 2016.
c) The limitation in selection of children gender.
d) The limitation in selection of the mothers that have children conduct disorder.
e) The limitation in organizing sessions on the bases of Adlerian approach.
Limitation out of researcher selection
a) Complete non-cooperation of mothers for active attendance in the initial sessions of training course.
b) Intimacy and mental position of mothers.
c) Economic and social position of mothers.
d) Little research and experimental background in the parent training field with Adlerian approach in Iran.
Suggestion of the study
The trained mothers to be identified in the light of the variables such as children's numbers, family difficulties and regarding girls in research group in order that the effectiveness of this method in special variety to be investigated.
The researcher’s suggestion for future researches:
a) This parent training method to be used in future researches and their result to be compared with to individual trainings.
b) This parent training method to be done with attendance of parents.
c) This parent training to be evaluated in longitudinal form in order that the correctness of results to be assured in the long period.
References
- Bloomquist ML (1996) Skill training for children with behavior disorder: a parent and therapist guide book.
- Klienke CL (1996) Coping with life challenges. XI(1-2): 27-29.
- Tynan WD, Jefferson TH (2006) Conduct Disorder. Available from, Specialties, Pediatrics, Developmental and Behavioral, 1-9.
- Minaei A (2005) Manual of ASEB school-age forms for Iranian children. Research Institution for Exeptional Children. Tehran.
- Barkely RA, Jensen PA, Menvielle E, Vitiello B (1996) Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH).
- Chandler J (2000) Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD) and Conduct Disorder (CD) in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis and Treatment.






























