The Solution of Discrepancy of Late Deceleration and the Prevention of Cerebral Palsy by the Hypoxia Index
Kazuo Maeda*
Honorary professor, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Tottori University Medical School, Japan
Submission: April 23, 2018; Published: May 08, 2018
*Corresponding author: Kazuo Maeda, Honorary professor, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Tottori University Medical School, Japan, Email: maedak@mocha.ocn.ne.jpHow to cite this article: Kazuo M.The Solution of Discrepancy of Late Deceleration and the Prevention of Cerebral Palsy by the Hypoxia Index. Curr Trends Biomedical Eng & Biosci. 2018; 14(2): 555883.DOI:10.19080/CTBEB.2018.14.555853
Solution of Fetal Heart Rate Discrepancy
Although the late deceleration (LD) of fetal heart rate (FHR) was ominous outcome sign in fetal monitoring [1], there was discreparency, namly, the neonatal outcome of 3 connective LDs was vigorous & normal, while the neonate afterrepeated LDs in 50 minutes was severe asphyxia, whose Apgar score was 3, and follwed by brain hemorrage & death 3 months later. However the difference was caused by the repetition of deceleration (transient fetal bradycardia) but not due to abnormal form of late deceleration.
Thus, the author intended to evaluate the sum of deceleration durations (min) divided by the lowest FHR (bpm, the hypoxic intensity) multiplied by 100, that was Maeda's hypoxia index (HI), which was the same as the hypoxic area (dip area), and it was the sum of hypoxic effects of repeated decelerations, that was as weak as 6 in 3 decelrations, but as strong as 26 after 50 minutes reprtitions. The LD discrepancy was solved by hypoxia index.
Preventin of Cerebral Palsy Caused by Intrapartum Hypoxic Fetal Damage
As fetal brain reacts fetal movements then heart rate inreases, fal brain reacts by fetal movenent group (movement bursts) forming acceieration (transient tachycardia), the acceleration disappears in early statge of hypoxia due to the suppression of fetal bain, while fetal brain reacts minor fetal movements,andforms FHR variability, which disappears at severe hypoxia after the loss of acceleration, the loss of variability is the most severe fetal hypoxia, that was the same as anencephalic fetus [2]. The hypoxia index of all 6 cases, whose variability was lost, developed severe fetal brain damage followed by cerebral palsy was 25 or more, whreas the hypxia index of 16 cases of normal variability and follwed by no cerebeal palsy hypoxia index of 6 cases of nrmal variabilty, no intrapartum brain damage, and followed by no cerebral palsy was 24 or less (Table 1).
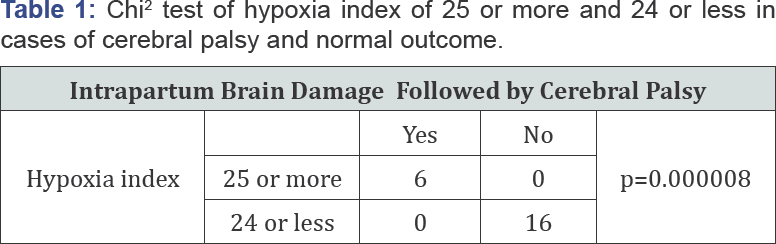
Thus, cerebral palsy caused by intrapartum hypoxic daage will be prevented, if hypoxia index is 24 or less.
Computerized Fetal Monitoring
FHR score, hypoxia index and FHR curve frequency spectrum will be included.
(1) FHR score calculated every 5 minutes.
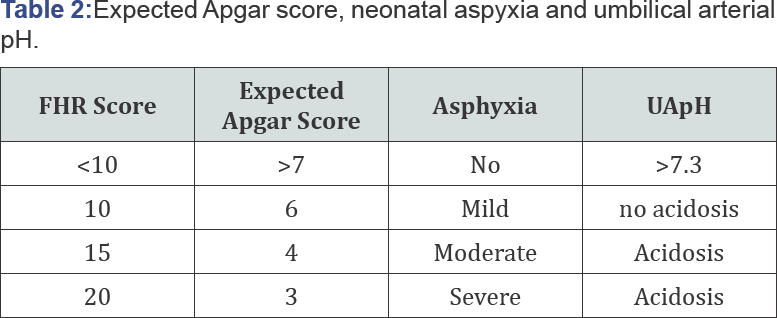
Apgar score and UApH are expected by regression equations. Direct report to doctor from computer (Table 2).
i. Hypoxia index
a) Direct report from computer to doctor when hypoxia index is positive.
b) Hypoxia index is reported every 5 minutes after positive hypoxia index.
c) Hypoxia index must be 24 or less at delivery.
d) No diagnosis of deceleration pattern (Observe FHR curve )
ii. Frequency spectrum data
a) Pathologic sinusoidal FHR and its La/Ta and PPSD values are reported doctor.
iii. Fetal hiccupping must be diagnosed in continuous spikes but no movement burst






























