Metazoan Parasites (Crustacea, Digenea and Monogenea) from Atlantic Black Skipjack Euthynnus alletteratus: A Checklist
Cláudio G da Silva1*, Naibe C de Figueiredo1 and Guelson B da Silva2
1Pós-graduação em Produção Animal, Centro de Ciências Agrárias, Universidade Federal Rural do Semi-Árido, Brasil
2Professor do Curso de Engenharia de Pesca, Centro de Ciências Agrárias. Universidade Federal Rural do Semi-Árido, Brasil
Submission: February 23, 2018; Published: March 26, 2018
*Corresponding author: CG da Silva, Laboratório de Sanidade Aquática, Centro de Ciências Agrárias, Universidade Federal Rural do Semi-Árido, Rio Grande do Norte, Brasil, E-mail: giovanio-sl@hotmail.comHow to cite this article: Cláudio G d S, Naibe C d F, Guelson B d S. Metazoan Parasites (Crustacea, Digenea and Monogenea) from Atlantic Black Skipjack Euthynnus alletteratus: A Checklist. Curr Trends Biomedical Eng & Biosci. 2018; 13(3): 555864.DOI:10.19080/CTBEB.2018.13.555864
Abstract
A checklist of the metazoan parasites of host fish Atlantic black skipjack (Euthynnus alletteratus) was compiled from parasitological records published between 1967 and 2018. The checklist is arranged alphabetically, providing valid names and authorities of the parasite species, its capture sites, author(s) and date of published records. A total of 18 valid species are listed from E. alletteratus. Parasite species where host data are missing or where the parasite was found not associated with a E. alletteratus not are included.
Keywords: Checklist; Fish parasites; Crustacea; Digenea; Monogenea
Introduction
The dispersion pattern of the parasites has been considered of great importance to the population dynamics of the parasite- host relationship [1,2]. Are the parasitic abundance dependent processes influence on survival and fertility of hosts [3].
Bullard et al. [4] mentioned that the behaviour of forming shoals facilitates the horizontal dispersion of the larvae in some species of fish. Various studies have been conducted over the years to determine the diversity and relative effect of parasitism in the world [5].
Parasites are now recognized as important components in global biodiversity [6], helping to understand the biology, survival, host population structure and ecosystem functioning, directly influencing fish populations by mortality or indirectly in reducing fecundity, behavioral changes, reduced swimming speed or increased risk of predation by the host [7].
The parasites Crustaceans are the most diverse and ubiquitous subphylum of arthropods in the seas. Most of the crustacean parasites are ectoparasites of a wide range of marine invertebrate and vertebrate organisms [8]. Monogeneans are a group of largely ectoparasitic members of the phylum Platyhelminthes. These worms are considered to be among the most host-specific parasites in fish, commonly found on fins, body skin, gills, gill chambers, buccal cavity, cornea and nostrils of their host [9]. Digeneans have a ventral or postero-ventral sucker, sometimes absent and the adults are primarily parasites of the gut, but they also occur free or incapsulated in the tissues of the vertebrates [10,11]
The Atlantic black skipjack Euthynnus alletteratus (Rafinesque, 1810) is a pelagic scombrid fish that inhabits the coastal tropical and subtropical waters of both sides of the Atlantic Ocean [12]. In the world, there is no checklist of parasites that infest the host fish Euthynnus alletteratus, which can generate deficiencies for the understanding of new studies.
This study is a start in correcting this deficiency by giving an updated checklist of the Metazoan parasites that infest the host fish Euthynnus alletteratus, using current and, as far as is possible to determine, correct nomenclature, can be a useful tool for studying the parasite distribution as well as the general parasite diversity in E. alletteratus, and it may also be an important tool for planning research activities in marine fish parasitology.
Methods
To compile the list parasites of Atlantic black skipjack Euthynnus alletteratus in the world, the records were obtained by searching the SciELO, Web of Science, Scopus, Springer, Elsevier, in the Portal of Periodicals CAPES / MEC and the mechanism of search of Google Scholar. To compile the data of the parasitic fauna of Atlantic black skipjack (E. alletteratus) data were compiled from the following studies: Palombi [13]; Cressey & Cressey [14]; Hendrix [15]; Fuentes [16]; Alves & Luque [17]; Chisholm & Whittington [18] and Mele et al. [12].
Checklist
This metazoan parasite checklist includes only Crustacea, Digenea and Monogenea. This checklist was compiled from records published between 1949 and 2016, covering a total of 7 papers. The papers analysed by us recorded 26 valid species parasitizing E. alletteratus. Reports of seven parasites that had not been identified to the species level were included in this checklist. Parasite species where host data are missing or where the parasite was found not associated with a E. alletteratus not are included. The results are presented as a list of parasite species in E. alletteratus (Table 1). The specific distribution of species in the host fish is also recorded.
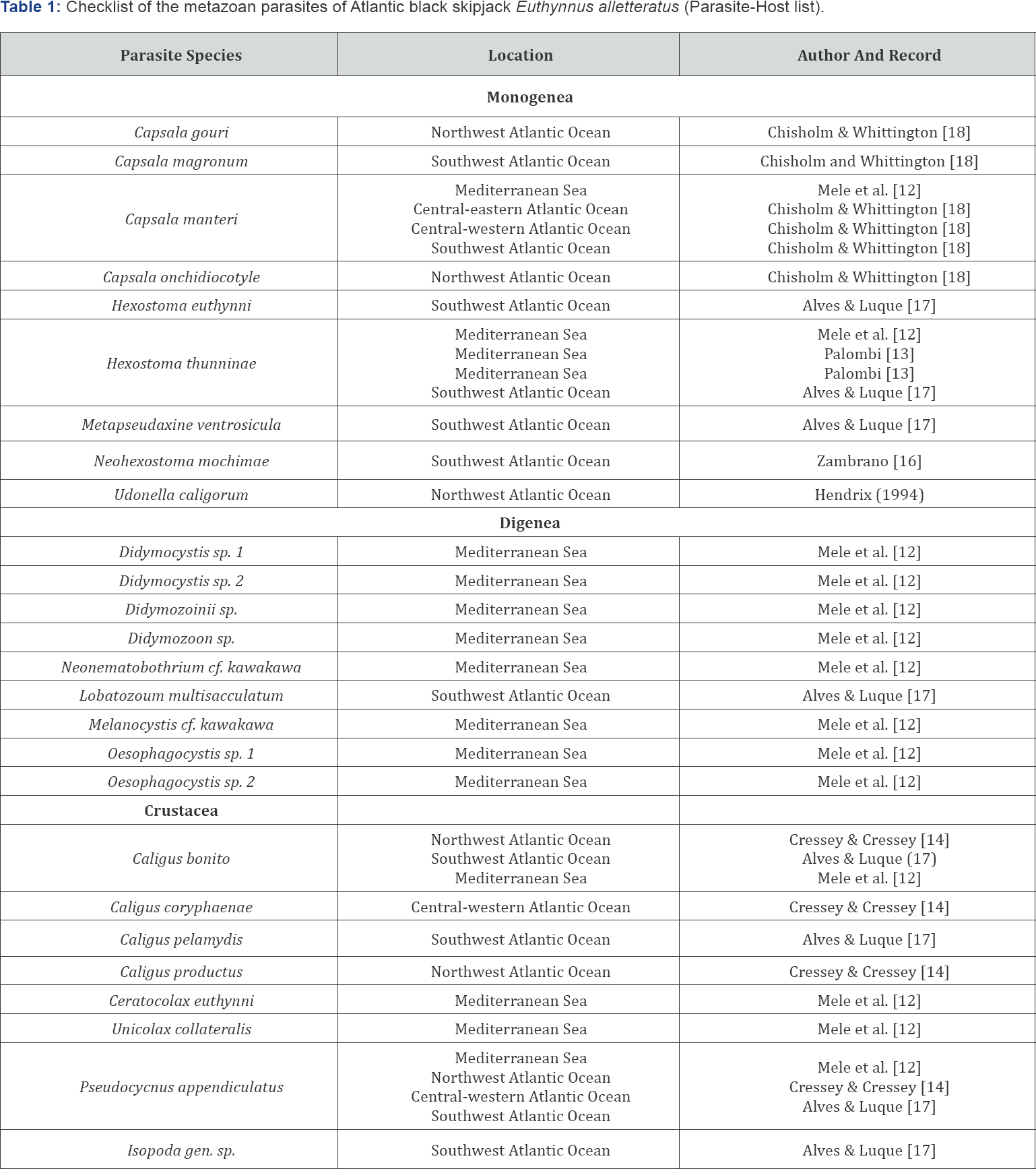
It is noticed the importance of literature review works, since it facilitates the work of future researchers, when there is a checklist of a certain species. During the research, it is understood that there are few researches in the branch of parasitology and mainly in Brazil there are few reports of parasite works of fish of the species E. alletteratus, even with this species inhabiting the entire Brazilian coast.
References
- Carvalho AR, Martins RT, Bellei PM, de Souza Lima S (2017) Aspectos ecologicos da helmintofauna de Hoplias malabaricus (Bloch, 1794) (Characiformes, Erythrinidae) da Represa Dr. Joao Penido (Juiz de Fora-MG, Brasil). Revista Brasileira de Zoociencias 18(1).
- Penczykowski RM, Laine AL, Koskella B (2016) Understanding the ecology and evolution of host-parasite interactions across scales. Evolutionary Applications 9(1): 37-52.
- Visser MD, Schnitzer SA, Muller-Landau HC, Jongejans E, de Kroon H, et al, et al. (2017) Tree species vary widely in their tolerance for liana infestation: A case study of differential host response to generalist parasites. J Ecol 0: 1-4.
- Bullard SA, Goldstein RJ, Hocking R, Jewell J (2003) A new geographic locality and three new host records for Neobenedenia melleni (MacCallum)(Monogenea: Capsalidae). Gulf and Caribbean Research 15(1): 1-4.
- Appeltans W, Ahyong ST, Anderson G, Angel MV, Artois T, et al. (2012) The magnitude of global marine species diversity. Curr Biol 22: 21892202.
- Cavalcanti ETS, Nascimento WS, Takemoto RM, Alves LC, Chellappa S (2013) Ocorrencia de crustaceos ectoparasitos no peixe ariaco, Lutjanus synagris (Linnaeus, 1758) nas aguas costeiras do Rio Grande do Norte. Biota Amazonia 3: 94-99.
- Longshaw M, Frear PA, Nunn AD, Cowx IG, Feist SW (2010) The influence of parasitism on fish population success. Fisheries Management and Ecology 17: 426-434.
- Rohde K (2005) Marine parasitology. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK, pp.1-590.
- Costa EF, Chellappa S (2016) First record of Amphipolycotyle chloroscombrus Hargis, 1957 (Monogenea, Polyopisthocotylea, Gastrocotylidae) in the South Atlantic Ocean. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography 64(1): 101-104.
- Cribb TH (2005) Digenea (endoparasitic flukes). In: Rohde K (Ed.), Marine parasitology. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK, 76-86.
- Bray RA, Gibson DI, Jones A (2008) Keys to the Trematoda. Vol. 3. CAB International and Natural History Museum, Wallingford, UK, 1-848.
- Mele S, Pennino MG, Piras MC, Macias D, Gomez-vives MJ, et al. (2016) Ecology of the Atlantic black skipjack Euthynnus alletteratus (Osteichthyes: Scombridae) in the western Mediterranean Sea inferred by parasitological analysis. Parasitology 143(10): 1330-1339.
- Palombi A (1949) I trematodi d'ltalia. Parte I. Trematodi monogenetici. Arch Zool Ital 34: 204- 408.
- R, Cressey HB (1980) Parasitic copepods of mackerel and tuna-like fishes (Scombridae) of the world. Smithson Contrib Zool 311: 1-186.
- Hendrix SS (1994) Marine flora and fauna of the eastern United States. Platyhelminthes: Monogenea. NOAA Technical Report NMFS 121, USA.
- Fuentes Zambrano JL (1997) Neohexostoma mochimae n. sp. y Pseudochauhanea elegans n. sp. (Monogenea) dos nuevas especies de parasitos de peces de la Bahi'a de Mochima, Venezuela. Bol Inst Oceanogr Venezuela 36: 45-52.
- Alves DR, Luque JL (2006) Ecologia das comunidades de metazoarios parasitos de cinco especies de escombri'deos (Perciformes: Scombridae) do litoral do estado do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Rev BrasParasitol 15: 167-181.
- Chisholm LA, Whittington ID (2007) Review of the Capsalinae (Monogenea: Capsalidae). Zootaxa 1559: 1-30.






























