The Production of Gardenia Reds- The Kinetically Controlled Gardenia Red-1 and the Thermodynamically Controlled Gardenia Red-2
Chiu-Lan Hsieh1, Wang-Chi Hsieh2, Yu-Wen Chen2, Charng-Cherng Chyau3 and Robert Y Peng3,4*
1Graduate Institute of Biotechnology, Changhua University of Education, Taiwan
2Day Spring Biotech Co., Ltd., Taiwan
3Research Institute of Biotechnology, Hungkuang University, Taiwan
4Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Taipei Medical University, Taiwan
Submission: April 01, 2017; Published: April 28 , 2017
*Corresponding author: Robert Y Peng, Research Institute of Biotechnology, Hungkuang University, Research Institute of Medical Sciences, Taipei Medical University, Taiwan, Tel: +886426318652; Email; ypeng@seed.nettw
How to cite this article: Chiu-Lan H, Wang-Chi H, Yu-Wen C, Charng-Cherng C, Robert Y P. The Production of Gardenia Reds- The Kinetically Controlled Gardenia Red-1 and the Thermodynamically Controlled Gardenia Red-2. Curr Trends Biomedical Eng & Biosci. 2017; 3(5): 555623. DOI: 10.19080/CTBEB.2017.03.555623
Introduction
Gardenia colors are widely used as food colorants. Gardenia blue (GB) is mainly synthesized via the conjugation reaction of genipin with alpha-amino acids [1] (Figure 1). Previously, we have demonstrated the chemical kinetics of the transformation of geniposide to geniposidic acid [2].
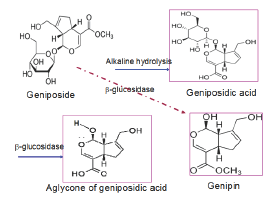
The production of Gardenia Red (GR) also has been demonstrated by [3] in which geniposidic acid (GPSA) was first deglucosidylated using the enzyme mixture (the main enzyme p -glucosidase with activity unit of 45.2Ug-1 was obtained from Aspergillus niger) at pH 4.5 and a temperature 40 �x00B0;C to form the alycone of geniposidic acid (AgGNPA), the latter then coupled with different kinds of amino acids to produce Gardenia Reds [3]. Dong synthesized GPSA in alkaline condition (pH 12) [4]. Moritome et al. [5] prepared purified extract from Gardenia fructus which was directly used for synthesis of GR. From our experience, the production of GR is handicapped by a variety factors, like the high content of genipin, the interfering amino acids and proteins.
Methods and Methods
Chemicals
Geniposide was purchased from Sigma Aldrich (purity>98%, St Louis, MO, USA). Other chemicals were provided by Wako Pure Chemicals (Osaka, Japan).
Preparation of GR: The modified method of [5] was followed to prepare GR. The final dextrin addition was omitted. The GR solution was purified by the adsorption macroporous adsorption resin (MinshengTMD101, China) and the desorption of color was eluted by ammonia solution (pH 10.0). The concentrated GR solution was lyophilized.
The powder GR (GR1) was re-dissolved in deionized water to a concentration 0.0001mg/mL and the opticall density of which was scanned with Elisa Reader within the range from 480 nm to 560nm. The product GR1 was then autoclaved at 121°C for 10 min to obtain GR2, which was similarly scanned using the same range of wavelength.
Results and Discussion
Effect of heating and autoclaving
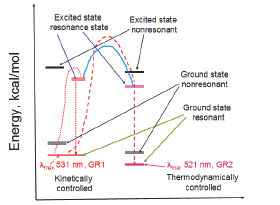
GR is thermal stable. The formation of GR1 was facilitated at 90 °C for 2h [5] (Figure 2). GR1 exhibited a maximum absorption at 531 nm (pmax=531 nm] with a color value of 2.12. When GR1 was subjected to autoclaving at 121 °C for 10 min, the Emax shifted to 521 nm (Figure 3), and the same time the color value increased to 3.90 (Figure 2).

Explanation in view of the physico-chemical aspects
Thus it is likely that GR1 is a product produced by kinetically controlled mechanism, while GR2 is the one called "thermally controlled" product. GR1 showed common red color, while GR2 looked more like a shining rose color (Figure 2 & 3). To our belief, this is the first time GR has been found to exhibit such an interesting phenomenon involving two different kinetic isomers.
References
- Park JE, Lee JY, Kim HG, Hahn TR, Young-Sook Paik YS (2002) Isolation and characterization of water-soluble intermediates of blue pigments transformed from geniposide of Gardenia jasminoides. J Agric Food Chem 50(22): 6511-6514.
- Xie JH, Liang HZ, Xu YZ, Tang BC (2011) Preparation of gardenia red pigment by hydrolysis of geniposidic acid with co-immobilized enzyme. Advanced Material Research 236(238): 1752-1756.
- Hsieh CL, Hsieh WC, Lin PX, Peng RY (2015) The inherent reactor kinetics for transformation of geniposidic acid from geniposide in a microreactor. Internl J Eng Res and Appl 5(1)(part 1): 42-65.
- Dong Z (2007) Preparation and refining of Gardenia Red. China Food Additives 2: 150-153.
- Moritome N, Kishi Y, Fujii S (1999) Properties of red pigments prepared from geniposidic acid and amino acids. J Sci Food Agric 79: 810-814.






























