A Comparative Study of Addition of Admixtures in Concrete Mix Design
Deepshikha Jain1* and Jay Shah2
1Department of Civil Engineering, Samrat Ashoka Technological Institute, India
2Center for Environmental Planning and Technology University
Submission: July 01, 2019; Published: July 12, 2019
*Corresponding Author: Deepshikha Jain, Department of Civil Engineering, Samrat Ashoka Technological Institute, India
How to cite this article: Deepshikha J, Jay S. A Comparative Study of Addition of Admixtures in Concrete Mix Design. Civil Eng Res J. 2019; 8(5): 555747. DOI: 10.19080/CERJ.2019.08.555747
Abstract
Cement possesses novel position among the cutting edge development materials, Concrete is a material utilized in structure development, comprising of a hard, artificially inactive particulate substance, known as a total (typically made of various sorts of sand and rock), that is fortified by bond and water. A blend plan method for elite cement blends has been displayed in this paper. Since rheological parameters and compressive quality are major properties of cement in two distinct phases of generation, the connection between rheological parameters and compressive quality has been utilized as opposed to utilizing water-bond proportion versus compressive quality relationship. Water-bond proportion and total volume to glue volume proportion has likewise been resolved from rheological conduct and utilized in the blend structure. In the proposed technique, the architect can evaluate parameters like compressive quality and efficient costing at the structure organize for a given target quality, notwithstanding elements of cement [1].
Keywords: Concrete mix design; Chemical admixtures; Water cement ratio; Portland cement
Introduction
Chemical admixtures are the ingredients in concrete aside from Portland cement, water, and mixture that are added to the combo forthwith before or throughout mix. Producers use admixtures primarily to scale back the price of concrete construction; to change the properties of hardened concrete; to make sure the standard of concrete throughout mix, transporting, placing, and curing; and to beat sure emergencies throughout concrete operations [2].
Successful use of admixtures depends on the utilization of applicable strategies of batching and concreting. Most admixtures square measure equipped in ready-to-use liquid type and square measure value-added to the concrete at the plant or at the jobsite. sure admixtures, like pigments, expansive agents, and pumping aids square measure used solely in very little amounts and square measure typically batched by hand from premeasured containers.
The effectiveness of AN admixture depends on many factors including: sort and quantity of cement, water content, mix time, slump, and temperatures of the concrete and air. Sometimes, effects almost like those achieved through the addition of admixtures may be achieved by fixing the concrete mixture-reducing the water-cement magnitude relation, adding extra cement, employing a totally different style of cement, or dynamical and aggregate gradation [3].
Admixtures are classed according to function. There are five distinct classes of chemical admixtures: air-entraining, water-reducing, retarding, accelerating, and plasticizers (superplasticizers). All other varieties of admixtures fall into the specialty category whose functions include corrosion inhibition, shrinkage reduction, alkali-silica reactivity reduction, workability enhancement, bonding, damp proofing, and colouring. Air-entraining admixtures, which are used to purposely place microscopic air bubbles into the concrete [4].
Steel Fiber

Steel fibre is a metal reinforcement. Steel fibre for reinforcing concrete is defined as short, discrete lengths of steel fibres with an aspect ratio (ratio of length to diameter) from about 20 to 100, with different cross-sections, and that are sufficiently small to be randomly dispersed in an unhardened concrete mixture using the usual mixing procedures Figure 1.
Glass Wool
Glass-fibre reinforced concrete (GRC) is a material made of a cementitious matrix composed of cement, sand, water and admixtures, in which short length glass fibres are dispersed. It has been widely used in the construction industry for nonstructural elements, like façade panels, piping and channels Figure 2.

SRB Latex
SBR LATEX is a carboxylate styrene butadiene copolymer latex admixture that is designed as an integral adhesive for cement bond coats, mortars and concrete to improve bond strength and chemical resistance Figure 3.

Rice Straw and Cement Bags Pieces

Rice straw was picked up from fields in jute bags. Rice straw was cut into small pieces with the help of chaff cutter, and then burned in the muffle furnace at controlled temperature. A total of 5% of cement was replaced with rice straw ash Figure 4.
Results and Discussions
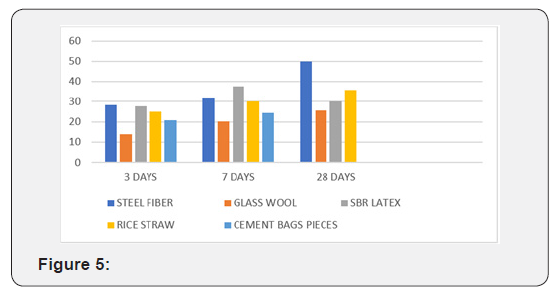
Conclusion
As per the results steel fiber give more strength on the concrete but its cost is higher, so instead of steel fiber we can use the rice straw and pieces of cement bags and get enough strength. Here we are getting more strength than the require strength in M25 grade so we can reduce the grade like M15 and get the target strength.
References
- Is 456 (2000) Plain and Reinforced Concrete-Code of Practice.
- Study of mix design of self-compacting concrete on m30 grade, Raghuveer, griet.
- Comparative study of concrete mix design by adding various types of admixtures, jay shah April 2014.
- https://www.cement.org/cement-concrete-applications/concrete-materials/chemical-admixtures






























